Comprehensive Guide on Autopsy Tool (Windows)
Autopsy is an open-source tool that is used to perform forensic operations on the disk image of the evidence. The forensic investigation that is carried out on the disk image is displayed here. The results obtained here are of help to investigate and locate relevant information. This tool is used by law enforcement agencies, local police and can also be used in the corporates to investigate the evidence found in a computer crime. It can likewise be utilized to recuperate information that has been erased.
Table of Contents
- Creating a New Case
- Data Sources
- Views
- File Type
- MIME-type
- Deleted Files
- MB File size
- Results
- Extracted Content
- Keyword Hits
- Timeline
- Discovery
- Images/Videos
- Add File Tags
- Generate Reports
So, let us get started! Download the Autopsy Tool from here.
Creating a new Case
Run the Autopsy tool on your Windows Operating System and click on “New Case” to create a new case.
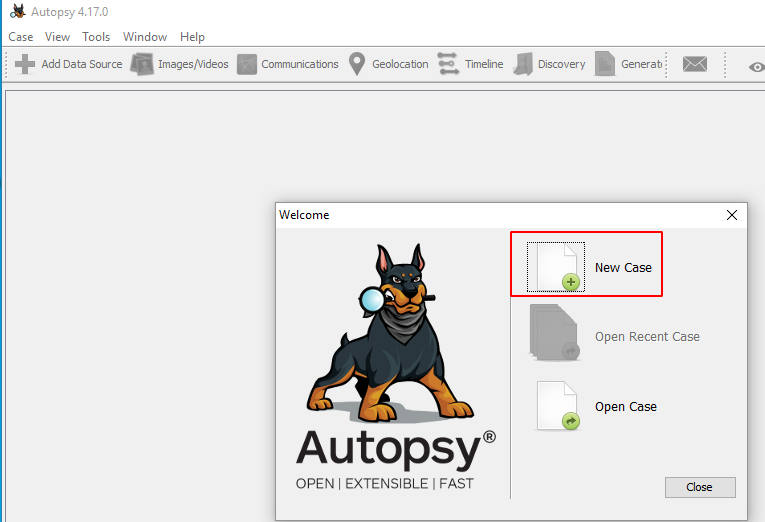
Then fill in all the necessary case information like the case name and choose a base directory to save all the case data in one place.
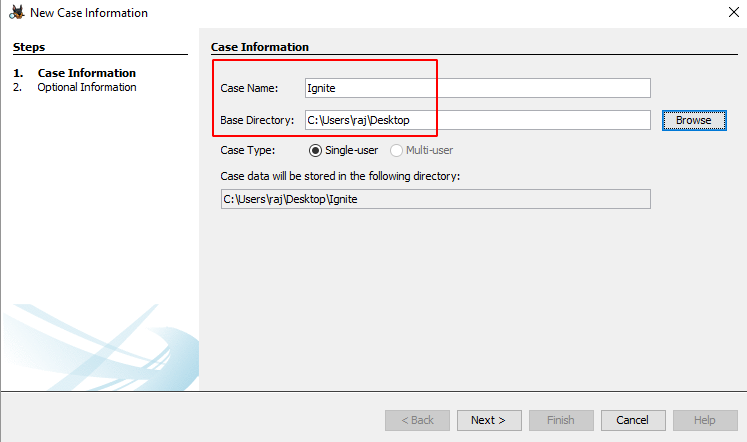
You can also add additional optional information about the case if required.

Now let us add the type of data source. There are various types to choose from.
Disk Image or VM file: This includes the image file which can be an exact copy of a hard drive, media card, or even a virtual machine.
Local Disk: This option includes devices like Hard disk, Pen drives, memory cards, etc.
Logical Files: It includes the image of any local folders or files.
Unallocated Space Image File: They include files that do not contain any file system and run with the help of the ingest module.
Autopsy Logical Imager Results: They include the data source from running the logical imager.
XRY Text Export: This includes the data source from exporting text files from XRY,
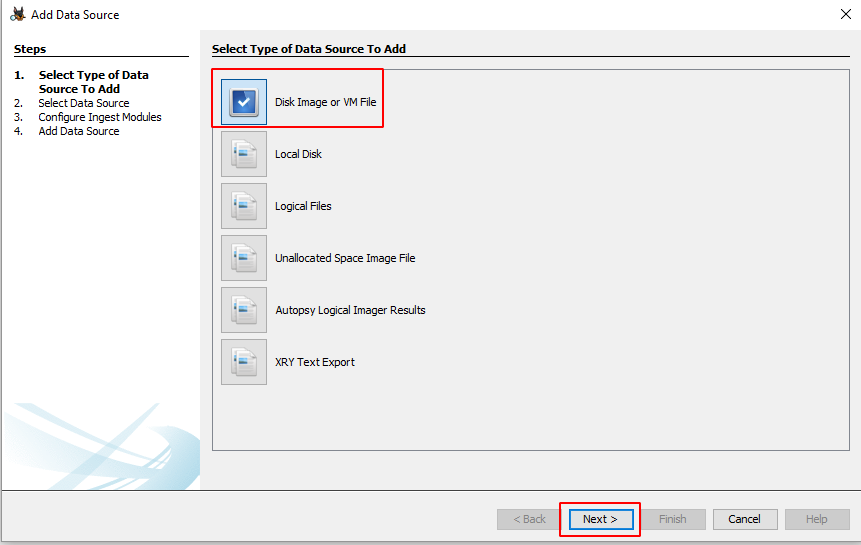
Now let us add the data source. Here we have a previously created image file, so we will add the location of that file.
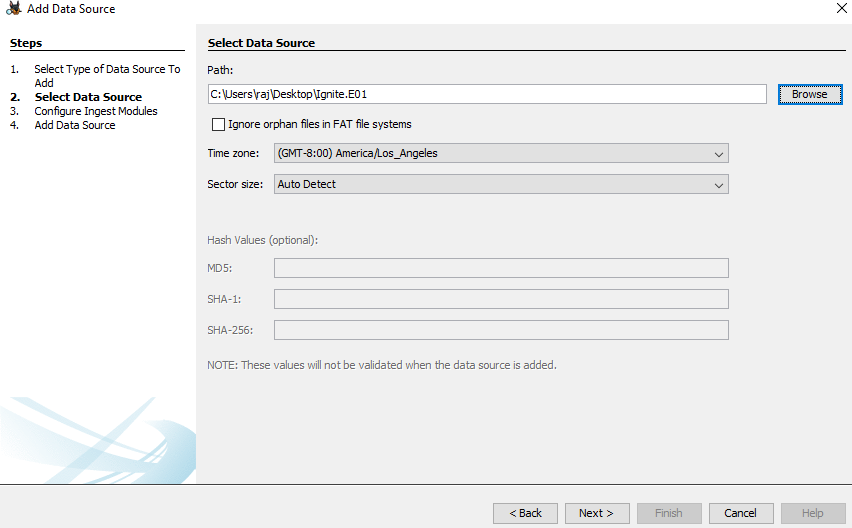
Next, you will be prompted to Configure the Ingest Module.

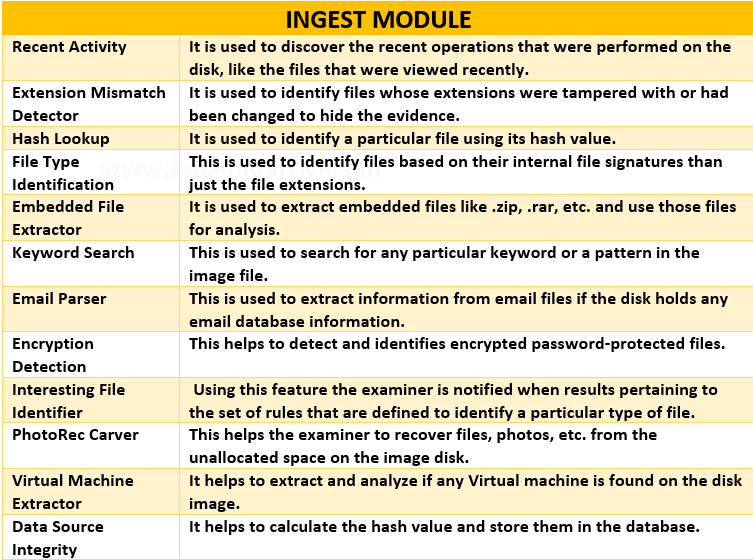
The contents of the Ingest module are listed below:
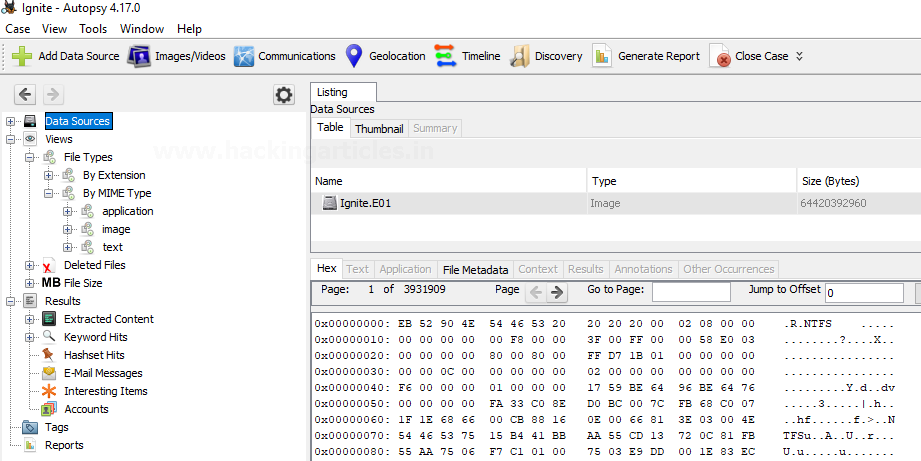
Data Source information displays basic metadata. Its detailed analysis is displayed at the bottom. It can be extracted one after the other.
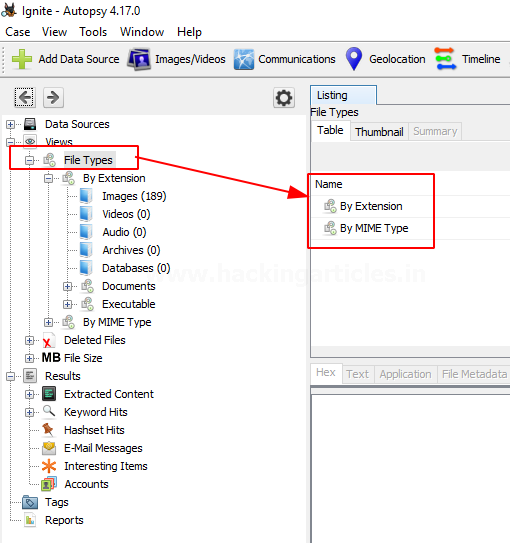
Views
File Type: It can be classified in the form of File extension or MIME type.
It provides information on file extensions that are commonly used by the OS whereas MIME types are used by the browser to decide what data to represent. It also displays deleted files.
Note: These file types can be categorized depending on Extension, Documents, Executables.
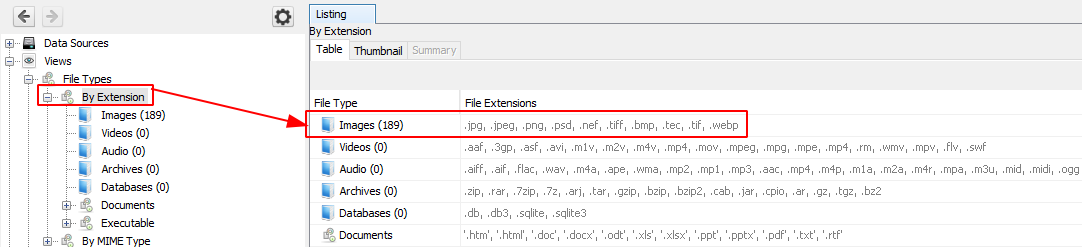
By Extension
In the category Filetypes by extension and you can see that this has been sub-divided into file types like images, video, audio, archives, databases, etc.
Let us click on images and explore the images that have been recovered.

We can also view the thumbnail of the images.
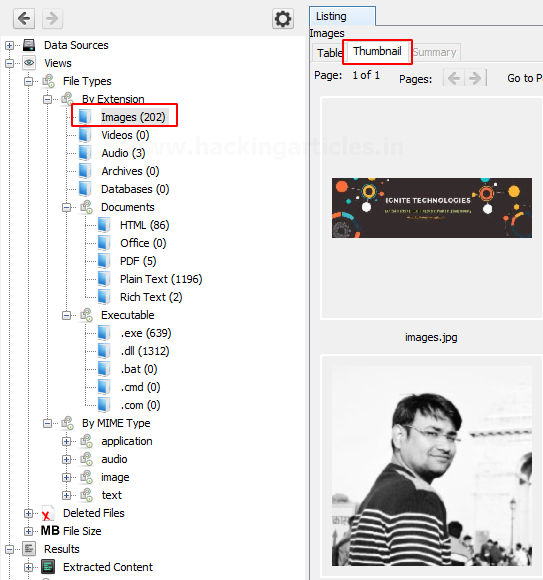
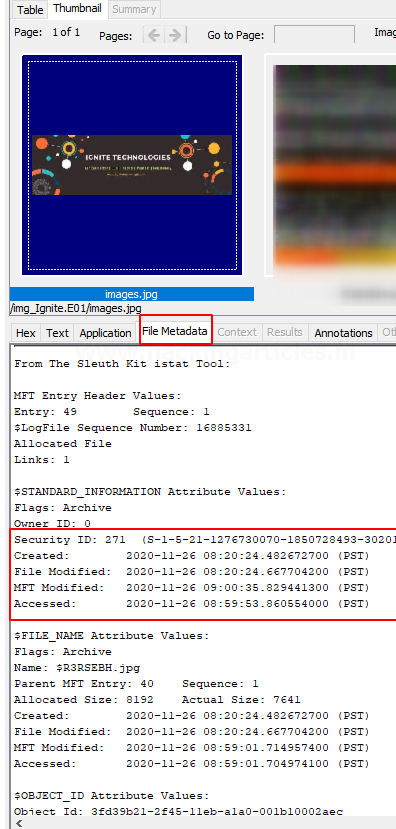
On viewing the thumbnail, you can view the file metadata and details about the image.
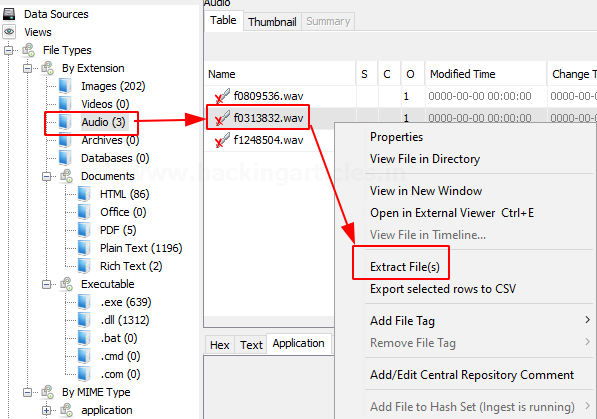
Here we can also view a few audio files that have been recovered. We can extract these files from the system and hear to them using various software.
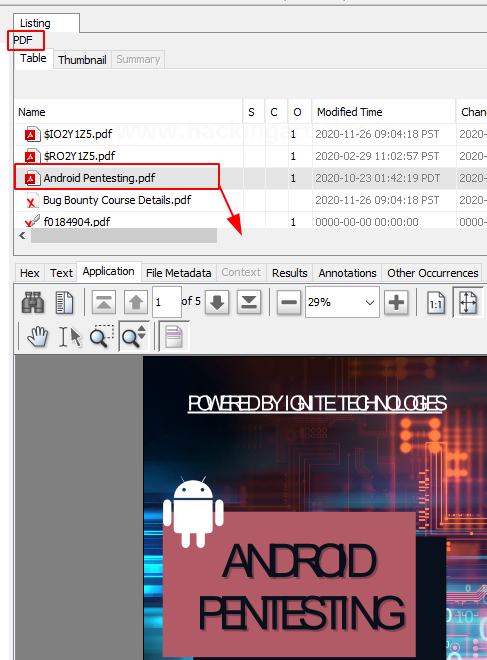
Documents
The documents are categorized into 5 types: HTML, office, PDF, Plain Text, Rich Text.
On exploring the documents option, you can see all the HTML documents present, you can click on the important ones to view them.

On exploring the PDF option, you can also find the important PDF in the disk image.
Similarly, the various Plain text files can also be viewed. You can also recover deleted plain text files.

Executables
These file types are then sub-divided into .exe, .dll, .bat, .cmd and .com.

By MIME Type
In this type of category, there are four sub-categories like application, audio, image, and text. They are divided further into more sections and file types.

Deleted Files: It displays information about the deleted file which can be then recovered.
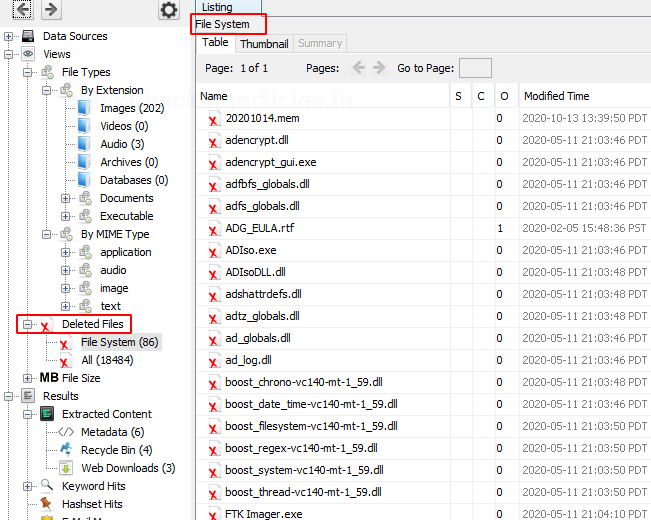
MB Size Files: In this, the files are categorized based on their size starting from 50MB. This allows the examiner to look for large files.

Results
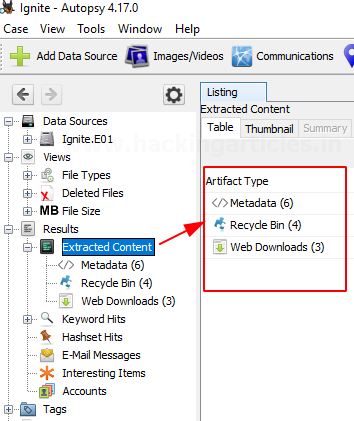
In this section, we get information about the content that was extracted.
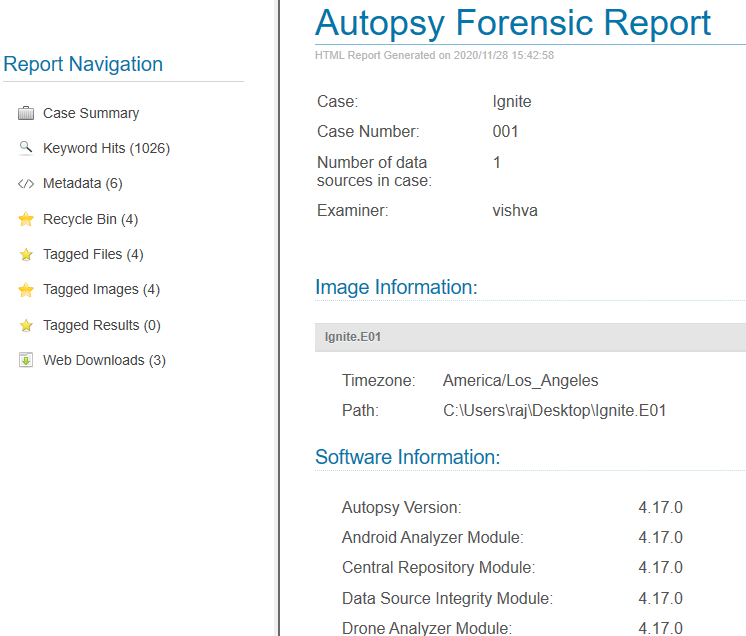
Extracted Content: All the content that was extracted, is segregated further in detail. Here we have found metadata, Recycle Bin, and web downloads. Let us further view each one of them.
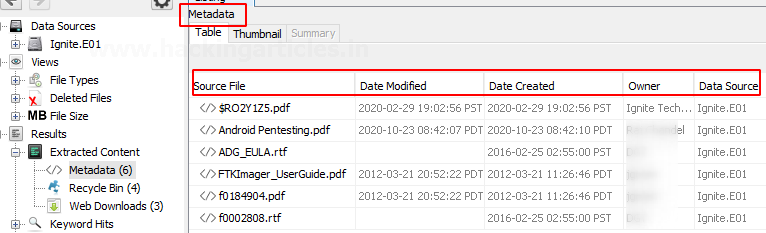
Metadata: Here we can view all the information about the files like the date it was created, to was modified, file’s owner, etc.
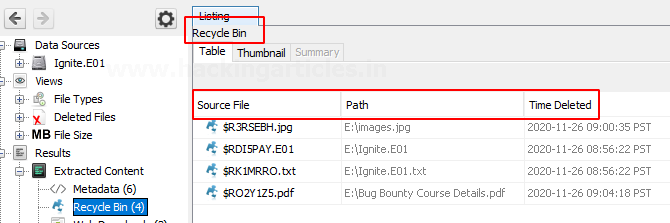
Recycle Bin: The files that were put in the recycle bin are found in this category.
Web Downloads: Here you can see the files that were downloaded from the internet.

Keyword Hits: In this, any specific keywords can be looked up for in the disk image. The search can be conducted concerning the Exact match, Substring matches, Emails, Literal words, Regular expressions, etc.

You can view the available email addresses.

You can choose to export into a CSV format.
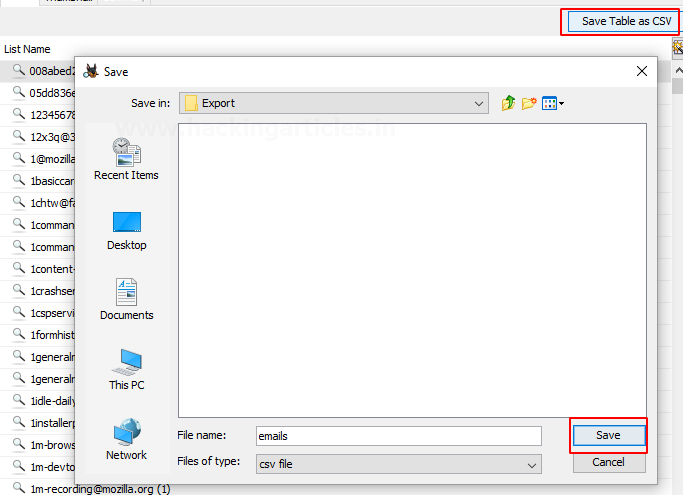
Timeline
By using this feature you can get information on the usage of the system in a statistical, detailed, or list form.

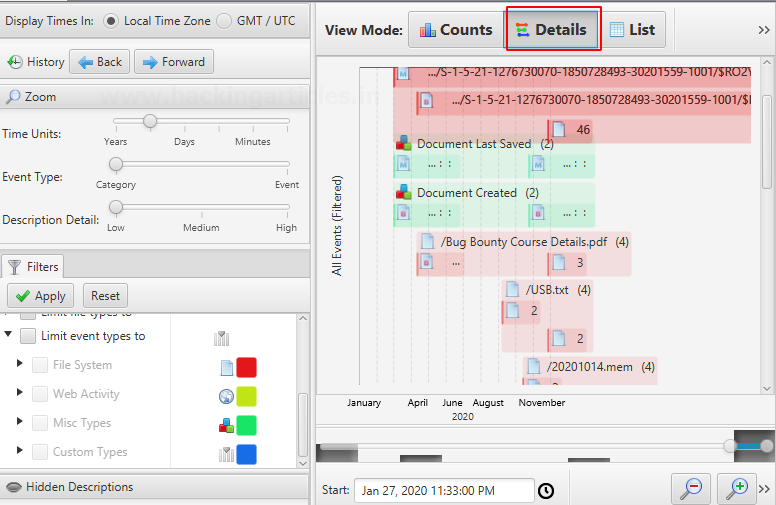

Discovery
This option allows finding media using different filters that are present on the disk image.

According to the selected options, you can get the desired results.

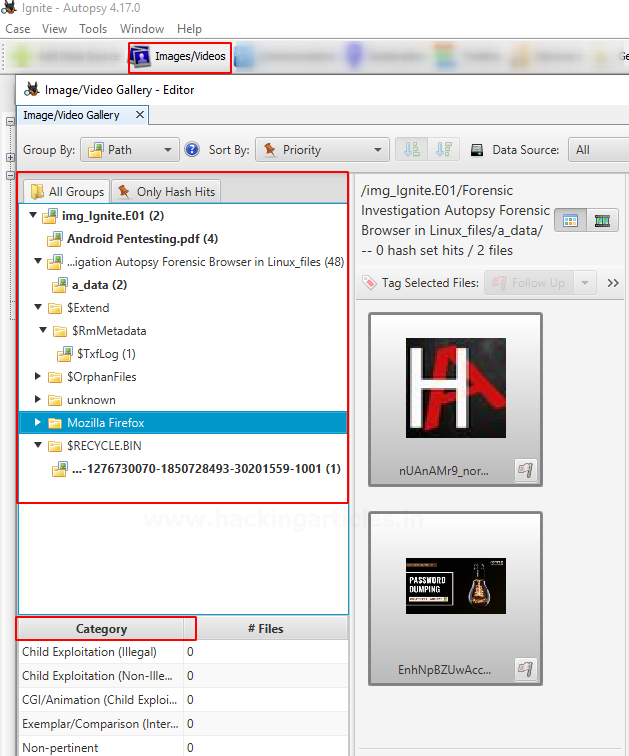
Images/Videos
This option is to find images and videos through various options and multiple categories
Add File Tag
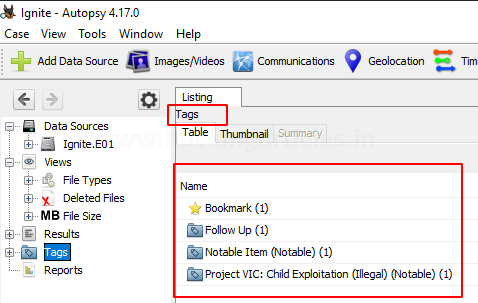
Tagging can be used to create bookmarks, follow-up, mark as any notable item, etc.

Now when you see the tags options, you will see that files were tagged according to various categories.
Generate Report
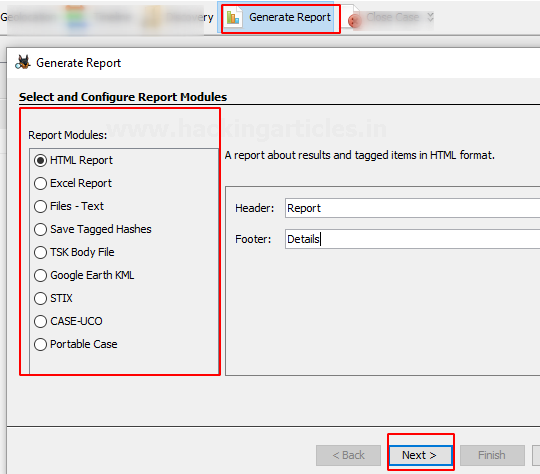
Once the investigation is done, the examiner can generate the report in various formats according to his preference.
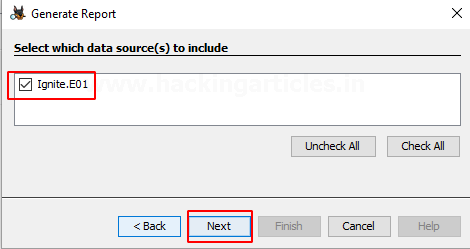
Check the data source whose report needs to be generated.
Here we chose to create the report in HTML format.
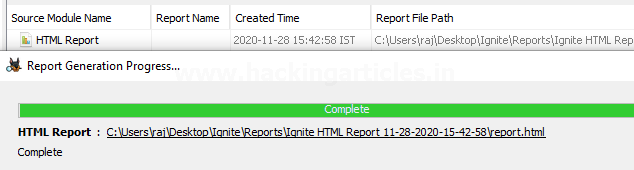
Kudos! Your Autopsy Forensic Report is ready!
Author: Vishva Vaghela is a Digital Forensics enthusiast and enjoys technical content writing. You can reach her on Here
Nice work