Understanding Log Analysis of Web Server
From Wikipedia
Logs
Log files are a standard tool for computer systems developers and administrators. They record the (W5) “what happened when by whom, where and why happened” of the system. This information can record faults and help their diagnosis.
Log Format
The Common Log Format also is known as the NCSA Common log format. Each line in a file stored in the Common Log Format has the following syntax:
[host; ident; authuser; date; request; status; bytes]
Example
127.0.0.1 user-identifier raj [30/Aug/2017:10:25:16 -0700] “GET /apache_pb.gif HTTP/1.0” 200 1068
- A “–” in a field indicates missing data.
- 0.0.1is the IP address of the client (remote host) which made the request to the server.
- User-identifier is the RFC 1413 identity of the client.
- raj is the user id of the person requesting the document.
- [30/Aug/2017:10:25:16 -0700] is the date, time, and time zone that the request was received
- “GET /apache_pb.gif HTTP/1.0” is the request line from the client.
- 200is the HTTP status code returned to the client. 2xx is a successful response, 3xx a redirection, 4xx a client error, and 5xx a server error.
- 2326is the size of the object returned to the client, measured in bytes
Importance of log analysis
Logs play an important role in tracking each client computer’s activity and its communication with other computers and networks. Network or system administrator analysis log in order to keep an eye on your network for vulnerabilities that may enter in the network to access sensitive information in the form of security attacks. You might be able to identify who introduces risks and help that person to use better precautions.
Location of log files
Generally, in Linux or UNIX system logs are created under /var/log directory, here you will find some very important log file such as Apache, auth, MySQL, kernel, bootstrap, dmeg, apt and etc.
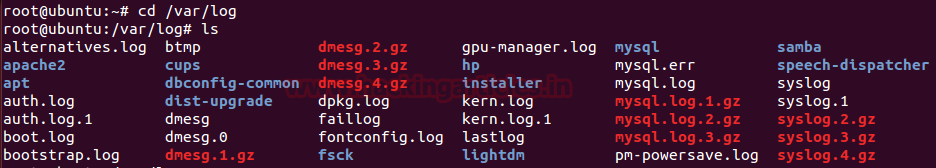
Some Important Types of Logs
Application log
The Application log contains events logged by applications or programs. For example, a database program might record a file error in the application log.
Apache: /var/log/apache
Samba: /var/log/samba
Mail: /var/log/
Mysql: /var/log/
For Example, let’s consider apache log files for analyzing its logs, there are two types of apache http server log files:
- Apache Access Log File
Apache server records all incoming requests and all requests processed to a log file. Location and content of the access to log /var/log/apache/access.log.
- Apache Error Log File
All apache2 errors information those are found during server requests is logged to this file. Location of error log /var/log/apache/error.log.
Now open apache2 log using the following command in terminal (UNIX system).
cd apache2 ls
You can see all log files of apache2 as shown in the given image.
echo > access.log
Using echo command I had deleted all previous logs from an inside access.log file so that we can read our recent logs for current activity.

As I had described above that apache2 will create logs for client activities on the browser. Therefore I had opened some web application like dvwa, BWapp and WordPress site in respective order and as result in same order log will be created inside apache2.

There are so many commands and tools used for log analyzing; among them, we had used only three command line utility cat, head and tail for reading logs.
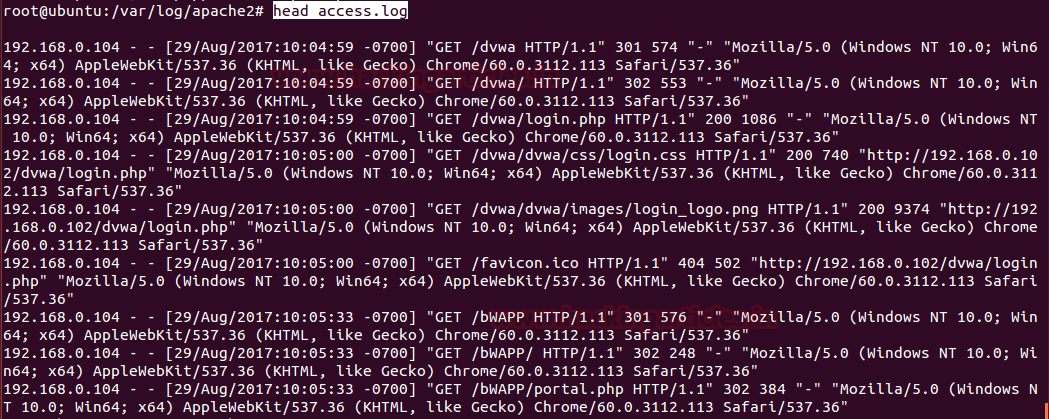
From the given image you can see we have used the cat command to read log which begins with dvwa’s log and end on WordPress log.
cat is standard UNIX utility use for reading the content of the file. With help of cat command, you can view whole content inside any log file.
Syntax: cat [options] file name
cat access.log

the head is a program on UNIX and Unix-like systems used to display the beginning of a text file.
Syntax: head [options] filename
head access.log
By default, the head will print the first 10 lines of its input to the standard output. Hence you can option [-n] for specific numbers of line. For example head – n 30 file name.
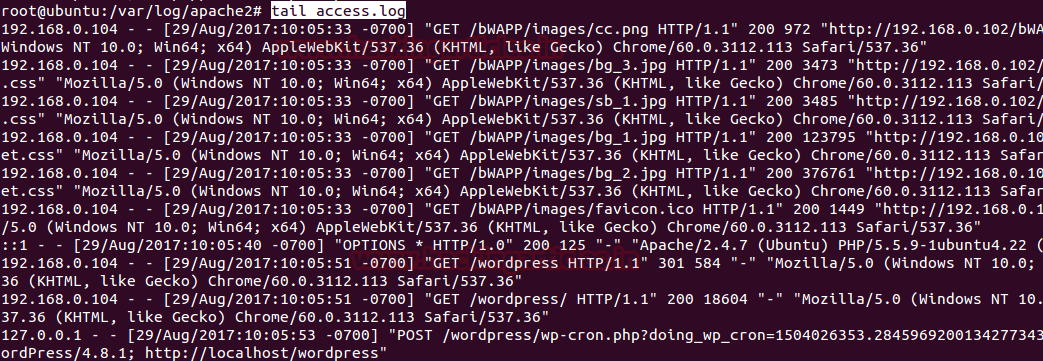
the tail is a program on UNIX and Unix-like systems used to display the tail end of a text file.
Syntax: tail [options] filename
tail access.log
From the given image you can perceive that it has shown log for WordPress at the end of the file.
A significant way of reading logs
Since tail reads end lines of the log file which consist information of recent activity of the client, therefore, we are going to take help tail’s option for reading log in a significant way.
By default, the tail will output the last 10 lines of its input to the standard output. Hence you can option [-n] for specific numbers of line. For example tail – n 30 file name.
tail -n 2 access.log
From the given image you can see above command applied filter and read only two logs from recent records.

If you want to read multiple log files simultaneously then type the following command.
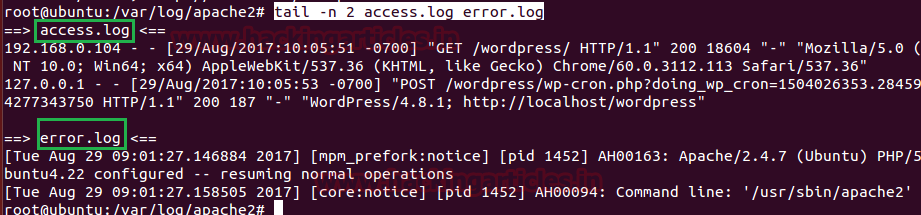
tail -n 2 access.log error.log
From the given image you can observe that it has shown two-two logs for each i.e. access log and error log.
Now apply the filter using grep command with the tail command for specific records of the log.
Syntax: tail [option] filename | grep “string” [option]
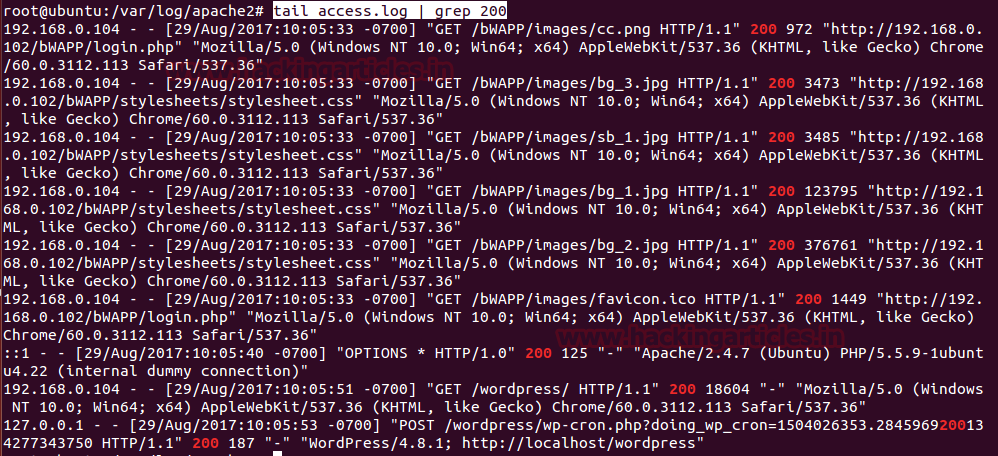
tail access.log | grep 200
From the given image you can notice, it has highlighted log having a string as 200. Generally, for a network administrator, this command will reduce his/her effort while log analyzing because he/she can directly read those log where client or attacker has got successfully response from the server.
When the server is not able to give reply of a request made by the client it response through error 404 “not found”.

tail access.log | grep 404
From the given image you can see it has highlighted log string 404 from a set of log records.

As you know on browser we had browsed web application DVWA, bWAPP and WordPress as respective sequences, therefore we get their log in the same sequence dvwa log at the top; bwapp log at middle and WordPress log at the end of access.log file
Log files are very large, reading them at ones will not possible for the administrator, therefore, he/she can use after and before option with grep as a filter for logs.
Syntax: tail [option] filename | grep -A [number of lines] “string”
tail access.log | grep -A 2 "bwapp"
Here -A stand for after, therefore it will filter 2 logs created after bwapp logs and hence it will indicate 2 logs of WordPress as shown in the given image.

Similarly, apply the filter using before parameter and type following command with a specific argument.
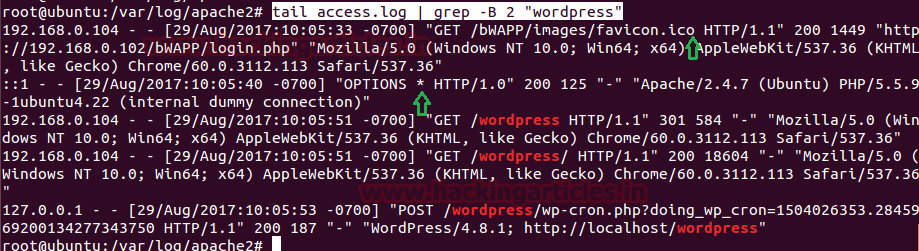
tail access.log | grep -B 2 "wordpress"
Here -B stands for before, therefore it will filter 2 logs created before WordPress logs and hence it will indicate 2 logs of bwapp as shown in the given image.
Auth Log
Auth.log file holds system authorization information; including user login attempts either successful or failure both type of log records as well as authentication method that were used for establishing a connection with the server, for example, SSH login between server and client
Location: /var/log
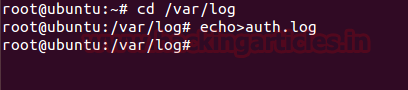
Again I had used echo command to remove all previous record from inside auth.log
echo>auth.log
Suppose the client uses putty for ssh login into the server.
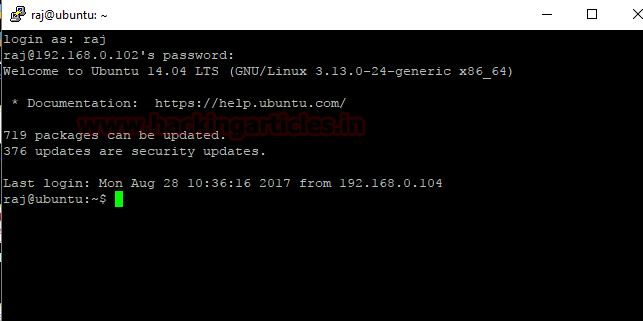
If the client having a valid credential for ssh then he will get successfully login into the server. From the given image you can see I had successfully login into the server. Hence inside server auth.log file, it will create a new record for SSH login successful.
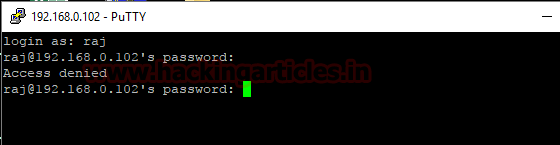
While in the next image you can read access denied message which means fail in login into an SSH server. Hence this time inside auth log again a new record will be created for SSH login failure.
Now let‘s read the whole records of the auth log file for above client activities using cat command.
cat auth.log
From the given image you can read the logs for successful and failed login.

Vsftpd Log
Vsftd log holds system authentication log for FTP login records either success or failure.
Location: /var/log
I had deleted all previous logs using echo command and using WinSCP for FTP server login. You can observe that we had login successfully. Hence it will create a new record in vsftpd.log for client login successfully.
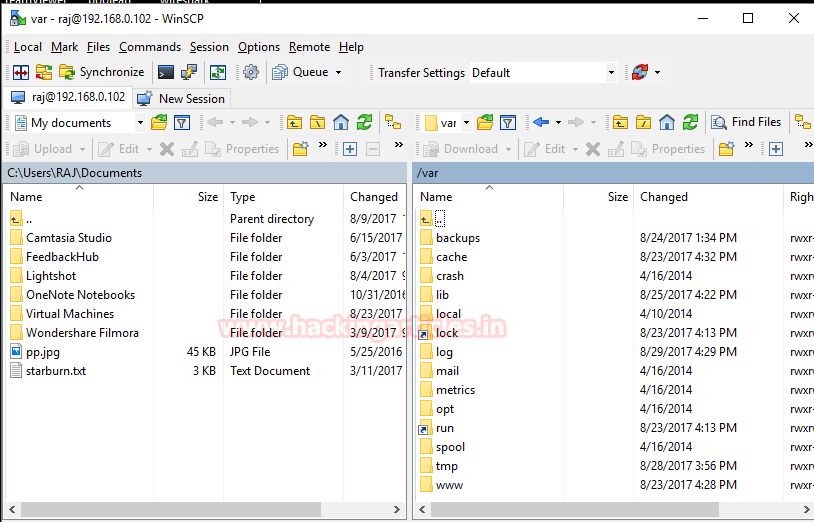
Now let’s verify it though vsftpd log file and use cat command for reading the whole file. From the given image you can observe it has created a record in the log file for client 192.168.0.104 is CONNECT.
cat vsftpd.log

System Log
syslog is a standard for system logs or message logging. The administrator may use syslog for system management and security auditing as well as general informational, analysis, and debugging messages. A wide variety of devices, such as printers, routers, and message receivers across many platforms use the syslog standard.
Location: /var/log
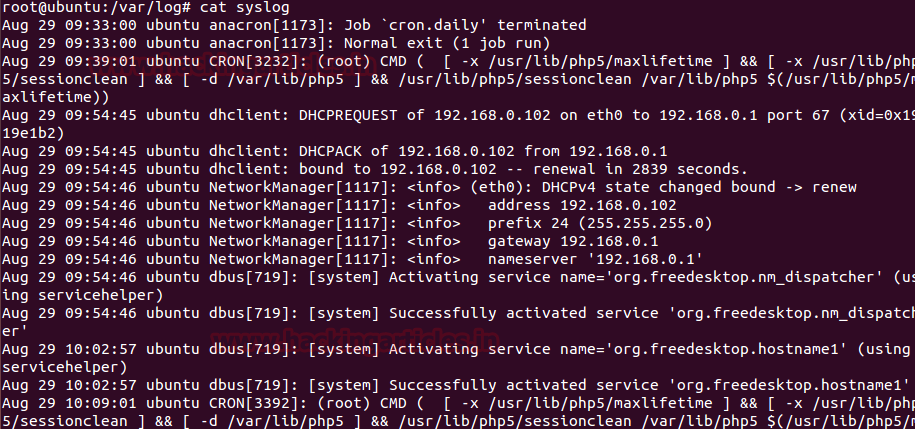
Use cat command for reading syslog as shown in the given image.
cat syslog
APT Log
The apt is a standard command-line tool in UNIX, which works for performing functions such as the installation of new software packages, upgrade of existing software packages, updating of the package list index, and even upgrading the entire Ubuntu system.
Location: /var/log
Hence apt contain its own log file for all new and previous installed software. It has two log file as:
- log : /var/log/apt
- log /var/log/apt
Now type the following command for reading history log of apt.
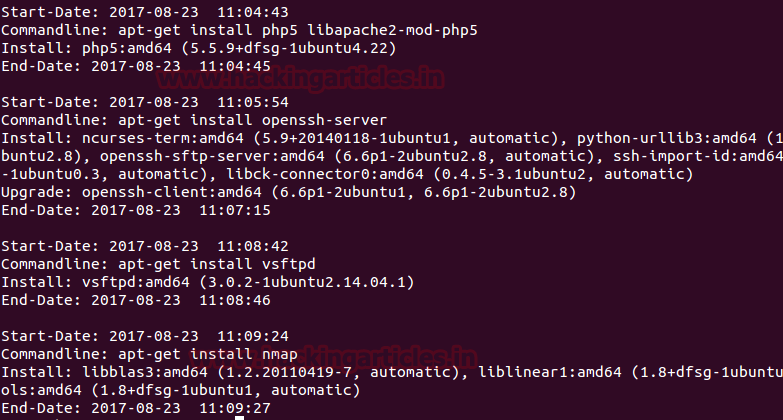
cat history.log
From the given image you can observe the result which contains information about software installation and updates.
It was a brief theory for reading logs in the simplest way.
Author: Aarti Singh is a Researcher and Technical Writer at Hacking Articles an Information Security Consultant Social Media Lover and Gadgets. Contact here
This is a very great article, good info and well written . Please share more such.