Nmap for Pentester: Host Discovery
Nmap has become one of the most popular tools in network scanning by leaving other scanners behind. Many times the hosts in some organisations are secured using firewalls or intrusion prevention systems which result in the failure of scanning due to the present set of rules which are used to block network traffic. In Nmap, a pentester can easily make use of alternate host discovery techniques to prevent this from happening. It consists of certain features that make the network traffic a little less suspicious. Hence, let us look at various techniques of Host Discovery.
Table of Content
- Ping Sweep ( No port scan)
- Disable-arp-ping
- Send-ip
- TCP Flags
- Types of Scans
- TCP SYN Ping Scan
- TCP ACK Ping Scan
- ICMP ECHO Ping Scan
- ICMP ECHO Ping Sweep
- UDP Ping Scan
- IP Protocol Ping scan
- ARP Ping Scan
- Traceroute
Ping Sweep
Let’s begin with scanning the entire network by using the Ping sweep scan (-sP).
nmap –sP 192.168.1.0/24
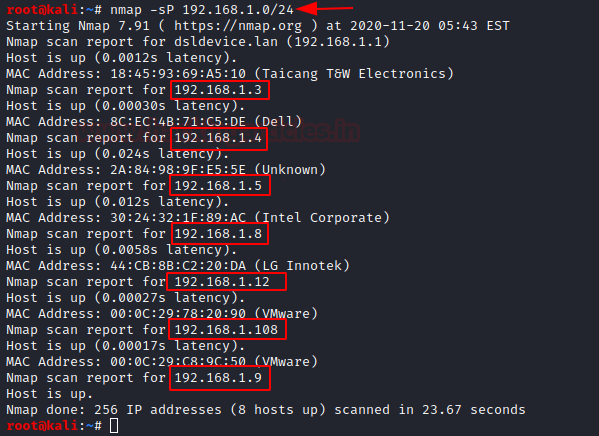
When you closely observe the packets in the Wireshark, you see that here only ARP packets are being sent while scanning the network,
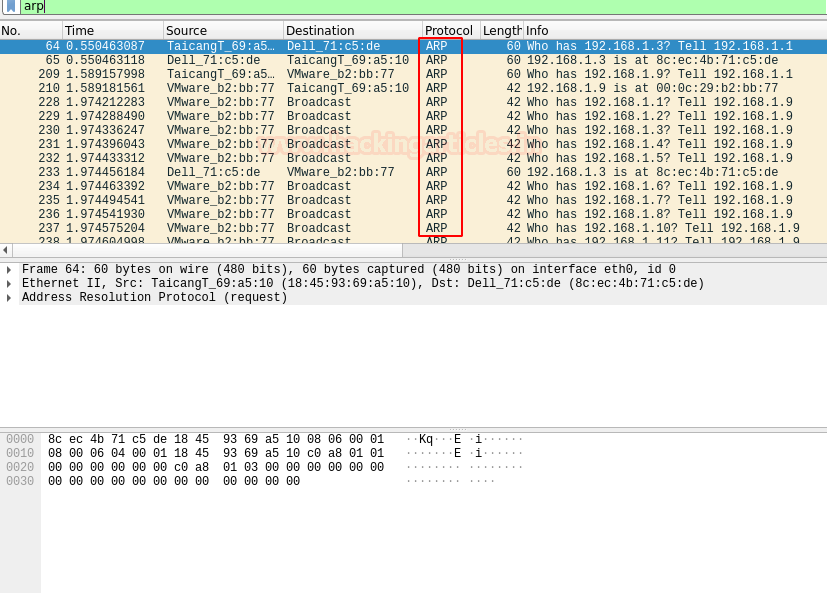
Note: Working of –sP and –sn is the same.
Let us try the same by using the no port scanning (-sn) option. In this option, we are also using –packet-trace option which will enable you to see the detailed packet transfer without making use of Wireshark. Here you can observe the ARP packets being received.
nmap -sn 192.168.1.0/24 --packet-trace
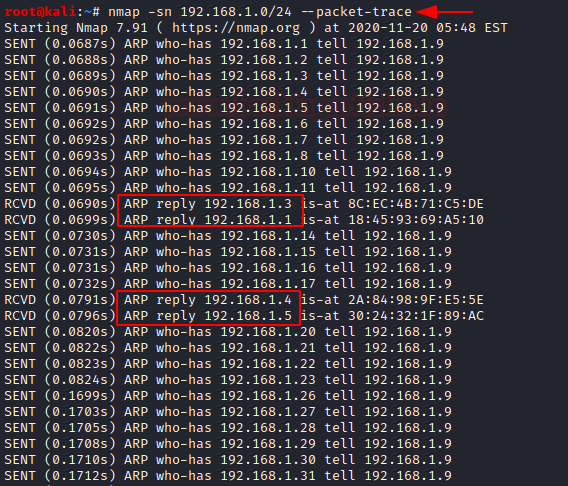
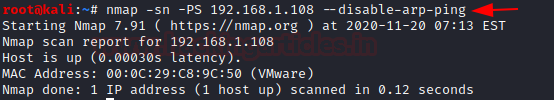
Now when we have seen that ARP packets are seen in the network, we will make use of –disable-arp-ping option where you can see that there are 4 packets being sent.
Disable-arp-ping
To disable the ARP discovery, Nmap provides this option.
nmap -sn 192.168.1.108 --disable-arp-ping

And you will see that the ARP packets are not visible
Note: Scanning Local Network with Nmap where nmap sends an ARP packet with every scan. If an external network is to be scanned; Nmap sends following request packets when –disable-arp-ping is used:


You can also make use of –send-ip option to get the same results as in the step above.
send-ip
nmap –sn 192.168.1.108 --packet-trace --send-ip
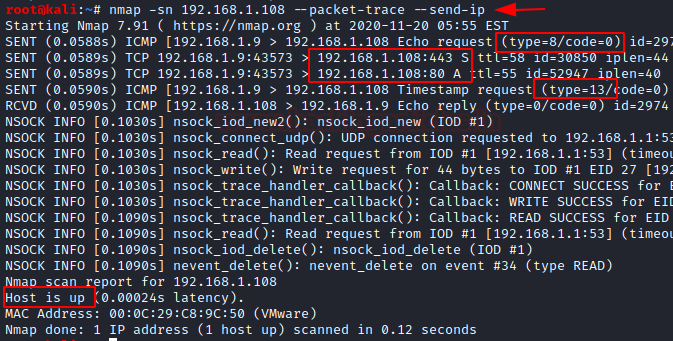
Host Discovery is considered to be the most primary step in Information Gathering which provides accurate results on active ports and IP addresses in a network.
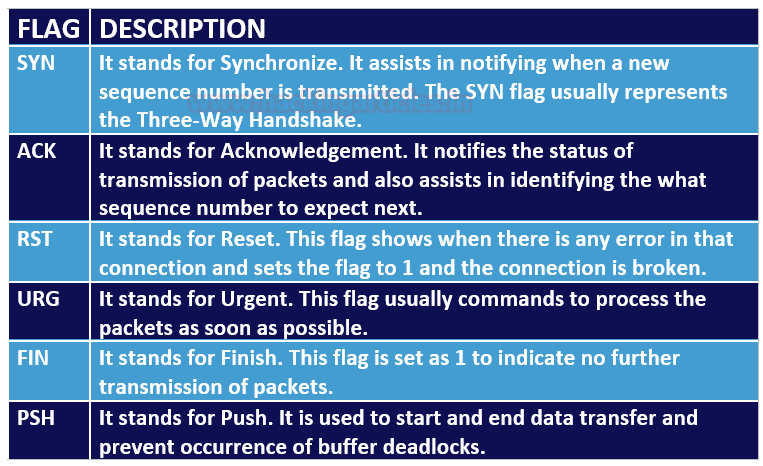
TCP Flags
First, let’s get to know the basics about the communication Flags in TCP. The TCP header mainly consists of six flags which manage the connection between the systems and provide instructions to them. Each flag is of 1 bit and hence the size of TCP Flags is 6 bits. Now let us briefly understand each flag.
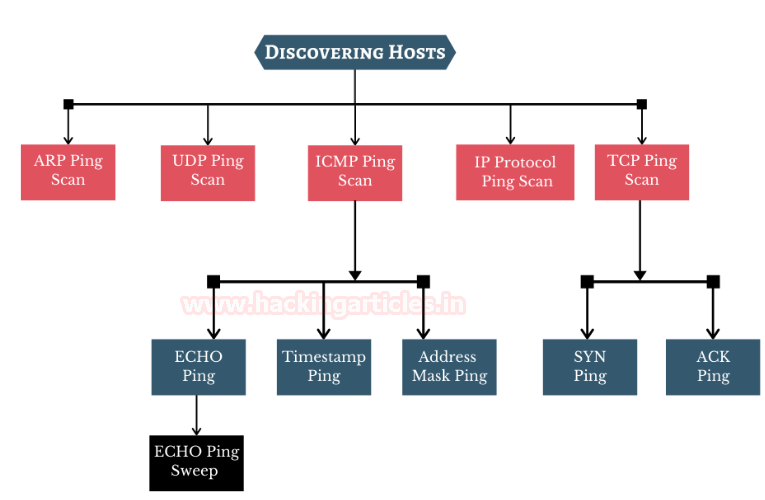
Types of Scans
To discover the hosts in the network, various ping scan methods can be used.
TCP SYN Ping Scan
It is a method of host discovery which helps in looking for discovering if the ports are open and to also make sure if it matches the rules of the firewall. The Pentester can hence, send an empty SYN flag to the target to check where it is alive. Multiple ports can be defined in this scan type.

The -sP command in Nmap only allows discovering online hosts. Whereas SYN Ping (-PS) sends a TCP SYN packet to the ports and if it is closed, the host responds with an RST packet. And if the ports requested are open there will be the response of TCP SYN/ACK and there will be a reset packet which will be sent to reset the connection.
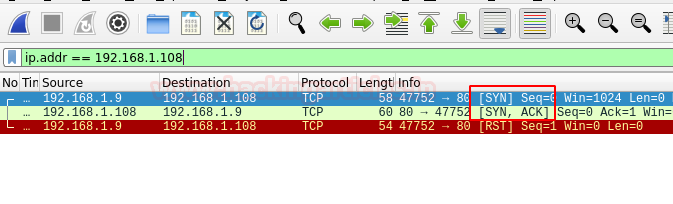
nmap -sn -PS 192.168.1.108 --disable-arp-ping
The packets captured using Wireshark can be overserved
The advantage of TCP SYN Ping scan is that the pentester can get the active/inactive status of the host without even creating a connection and hence it does not even create a log in the system or the network.
TCP ACK Ping Scan
It is a method of host discovery which is similar to TCP SYN Ping scan but slightly differs. This scan also makes use of Port 80. The pentester sends an empty TCP packet to the target and as there is no connection between them, it will receive an Acknowledgement packet and will then reset and terminate the request

This command is used to determine the target’s response and also check if the SYN packets or ICMP echo requests are blocked as of in the latest firewalls
nmap -sn -PA 192.168.1.108 --disable-arp-ping

The Packets captured in the Wireshark can be observed here.
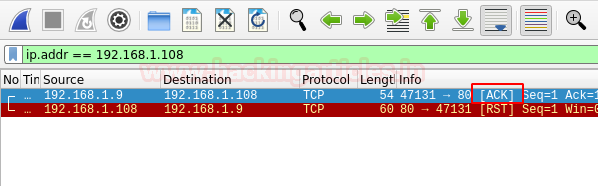
Some firewalls are configured to block on SYN ping packets, hence, in this case, this scan would be effective to bypass the firewall easily.
ICMP Echo Ping Scan
The ICMP Ping scan can be used to gather information about the target systems which makes it different from port scanning. The pentester can send an ICMP ECHO request to the target and getting an ICMP Echo reply in return.

ICMP is now ineffective on remote ICMP packets which have been blocked by admins. It can still be used to monitor local networks.
nmap -sn -PE 192.168.1.108 --disable-arp-ping

The packets captured in the Wireshark can be observed.

ICMP ECHO Ping Sweep
It is similar to Echo Ping Scan and is used to scan the active hosts from a given range of IP addresses. It sends ICMP requests to a huge number of targets and if a particular target is alive then it will return an ICMP reply.
nmap -sn -PE 192.168.1-10
ICMP Address Mask Scan
It is an older method of ICMP ECHO ping scanning. It gives out the information about the system and its subnet mask.
nmap -sn -PM 192.168.1.108 --disable-arp-ping

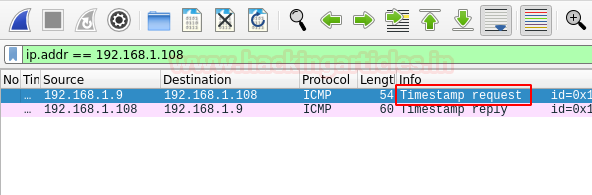
ICMP ECHO Timestamp scan
The pentester can adopt this technique in a particular condition when the system admin blocks the regular ICMP timestamp. It is usually used in synchronization of time.
nmap -sn -PP 192.168.1.108 --disable-arp-ping
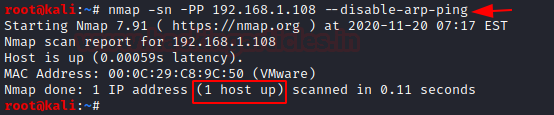
The packets captured using Wireshark can be observed.
UDP Ping Scan
The UDP Ping Scans uses a highly uncommon default port number 40125 to send packets to the target. It is similar to TCP Ping scan. The Pentester will send the UDP Packets to the target and if there is a response in return which means that the host is alive or else it is offline
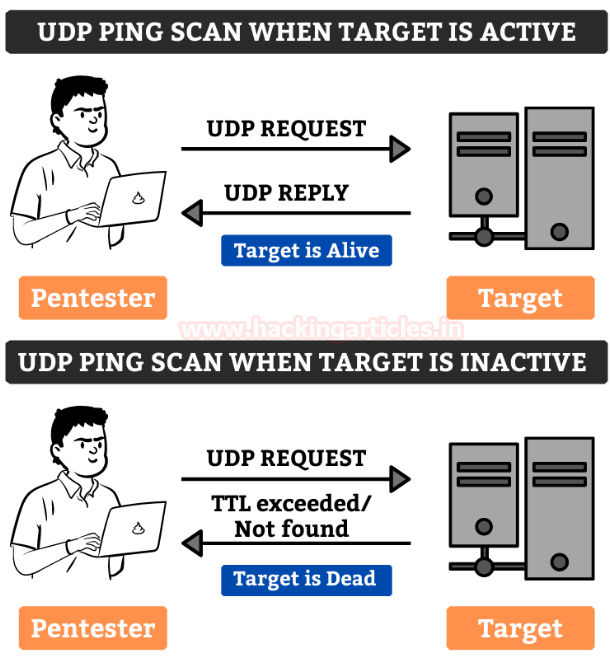
The advantage of UDP scan is that it can detect the systems which have firewalls with strict TCP rules and leaving UDP rules at ease.
nmap -sn -PU 192.168.1.108 --disable-arp-ping

You can observe the packets sent using Wireshark.

IP protocol ping scan
In this method, the pentester sends various packets using different IP protocols and hopes to get a response in return if the target is alive.

nmap -sn -PO 192.168.1.108 --disable-arp-ping

The packets captured can be observed using Wireshark.

No ping scan
In this method, host discovery is completely skipped. The pentester can use it to determine active machines for heavier scanning and to increase the speed of the network.
nmap -sn -PN 192.168.1.108 --disable-arp-ping

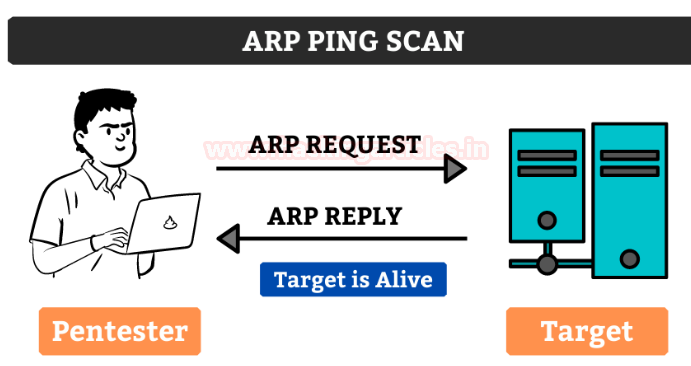
ARP ping scan
In this method, the ARP packets are sent to all the devices I the network although they are invisible due to the firewall. It is considered to be extremely efficient than other host discovery. It is mainly used for system discovery. It also mentions the latency.
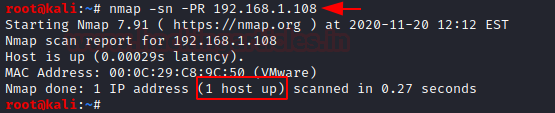
nmap -sn -PR 192.168.1.108
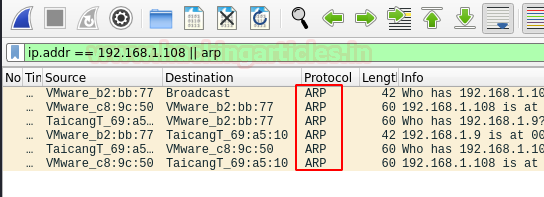
You can see the packets being captured in wireshark.
SCTP INIT Ping
It sends SCTP packet containing a minimal INIT chunk. Its default destination port is 80. The INIT chunk provides suggestion to the remote system that the pentester is attempting to establish an association.
nmap -sn -PY 192.168.1.108 --disable-arp-ping
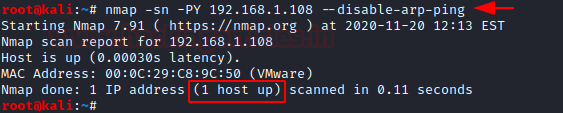
The packets that are captured can be observed.

Traceroute
Traceroutes are used after finishing scanning, by using the information from the scan results and to determine the port and protocol which will reach the target.
nmap -sn --traceroute 8.8.8.8

To get more information Traceroute you can refer to
Working of Traceroute using Wireshark
Reference: https://nmap.org/book/man-host-discovery.html
Author: Jeenali Kothari is a Digital Forensics enthusiast and enjoys technical content writing. You can reach her on Here
Most websites now have defence against NMap so its no good for some sites.
Very good article
kindly suggests me youtube courses to become kali Linux expert for penetration,hacking ,network security etc.
nicely explained