Understanding HTTP Authentication Basic and Digest
HTTP authentication uses methodologies via which web servers and browsers securely exchanges the credentials like usernames and passwords. HTTP authentication or we can also call it as Digest Authentication follows the predefined methods/standards which use encoding techniques and MD5 cryptographic hashing over HTTP protocol.
In this article, we are covering the methodologies/standards used for HTTP Authentication.
For the sake of understanding, we will be using our php scripts that will simply capture user name and passwords and we will generate the Authorization value as per the standards.
For http codes visit here
Basic Access Authentication using Base 64 Encoding
In basic Authentication, we will be using base 64 encoding for generating our cryptographic string which contains the information of username and password. Please note we can use any of the encoding techniques like URL, Hexadecimal, or any other we want.
The below example illustrates the concept, we are using Burpsuite for capturing and illustrating the request.
The webpage is asking for input from the client

We are providing “hackingarticles” as User Name and “ignite” as a password.
The syntax of Basic Authentication
Value = username:password
Encoded Value = base64(Value)
Authorization Value = Basic <Encoded Value>
In basic authentication username and password are combined into a single string using a colon in between.
Value = hackingarticles:ignite
This string is then encoded using base 64 encoding.
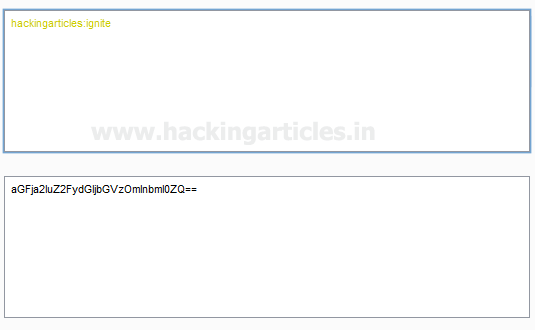
Encoded Value = base64 encoded value of hackingarticles:ignite which is aGFja2luZ2FydGljbGVzOmlnbml0ZQ==
Finally, the Authorization Value is obtained by putting the text “Basic” followed by <space> before the encoded value. (We can capture the request using burpsuite to see the result)

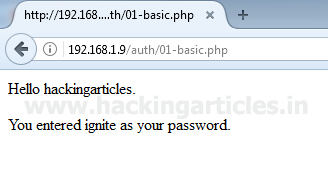
The Authorization Value for this example is “Basic aGFja2luZ2FydGljbGVzOmlnbml0ZQ==“. This is the value which is sent to the server.
Finally, the server is decrypting the authorization value and returning the entered credentials
Basic Authentication is a less secure way because here we are only using encoding and the authorization value can be decoded, In order to enhance the security we have other standards discussed further.
RFC 2069 Digest Access Authentication
Digest Access Authentication uses the hashing methodologies to generate the cryptographic result. Here the final value is sent as a response value.
RFC 2069 authentication is now outdated now and RFC2617 which is an enhanced version of RFC2069 is being used.
For the sake of understanding the syntax of RFC 2069 is explained below.
Syntax of RFC2069
Hash1=MD5(username:realm:password) Hash2=MD5(method:digestURI) response=MD5(Hash1:nonce:Hash2)
Hash1 contains the MD5 hash value of (username:realm:password) where the realm is any string
provided by server and username and passwords are the input provided by the client.
Hash2 contains the MD5 hash value of (method:digestURI) where a method could be got or post depending on the page request and digestURI is the URL of the page where the request is being sent.
the response is the final string which is being sent to the server and contains the MD5 hash value of (hash1:nounce:hash2) where hash1 and hash2 have generated above and nonce is an arbitrary string that could be used only one time provided by the server to the client.
RFC 2617 Digest Access Authentication
RFC 2617 digest authentication also uses MD5 hashing algorithm but the final hash value is generated with some additional parameters
Syntax of RFC2617
Hash1=MD5(username:realm:password) Hash2=MD5(method:digestURI) response=MD5(Hash1:nonce:nonceCount:cnonce:qop:Hash2)
Hash1 contains the MD5 hash value of (username:realm:password) where realm is any string
Provided by server and username and passwords are the input provided by the client.
Hash2 contains the MD5 hash value of (method:digestURI) where a method could get or post depending on the page request and digestURI is the URL of the page where the request is being sent.
the response is the final string which is being sent to the server and contains the MD5 hash value of (Hash1:nonce:nonceCount:cnonce:qop:Hash2) where Hash1 and Hash2 are generated above
and for more details on other parameters refer to ” https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc780170(v=ws.10).aspx”
The actual working of RFC2617 is described below
The webpage is asking for input from the client
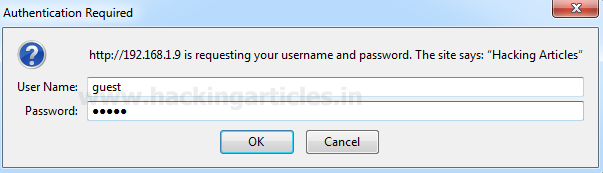
We are providing “guest” as User Name and “guest” as a password.
Through burpsuite, we are capturing the request so that all the parameters could be captured and we can compare the hash values captured with the hash values that we will generate through any other tool (hash calculator in this case).

We have captured the values for the following parameters
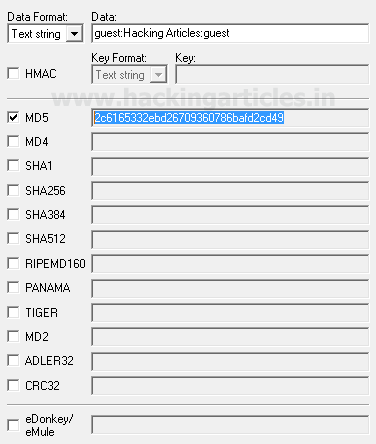
realm="Hacking Articles", nonce="58bac26865505", uri="/auth/02-2617.php", opaque="8d8909139750c6bd277cfe1388314f48", qop=auth, nc=00000001, cnonce="72ae56dde9406045" , response="ac8e3ecd76d33dd482783b8a8b67d8c1", Hash1 Syntax=MD5(username:realm:password) hash1 = md5(guest:Hacking Articles:guest)
The MD5 hash value is calculated as 2c6165332ebd26709360786bafd2cd49
Hash2 Syntax =MD5 (method:digestURI)
Hash2=MD5 (GET:/auth/02-2617.php)

MD5 hash value is calculated as b6a6df472ee01a9dbccba5f5e6271ca8
response Syntax = MD5(Hash1:nonce:nonceCount:cnonce:qop:Hash2) response = MD5(2c6165332ebd26709360786bafd2cd49:58bac26865505:00000001:72ae56dde9406045:auth:b6a6df472ee01a9dbccba5f5e6271ca8)
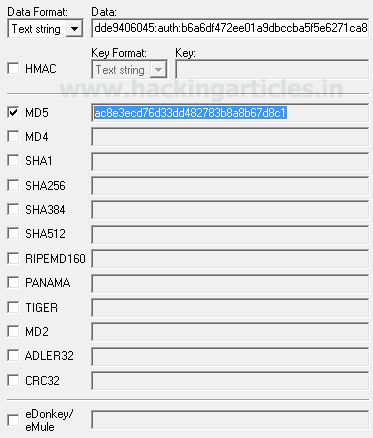
MD5 hash is calculated as ac8e3ecd76d33dd482783b8a8b67d8c1
Finally, the response value obtained through the hash calculator is exactly the same as that we have captured with burp suit above.
Finally, the server is decrypting the response value and the following is the result

Author: Ankit Gupta, the Author, and co-founder of this website, An Ethical Hacker, Telecom Expert, Programmer, India. He Has Found his Deepest Passion To Be Around The World Of Telecom, ISP and Ethical Hacking. Contact Here
You mentioned server is decrypting the response value. How can the server decrypt an MD5 hash?
Please explain as i am need of this understanding urgently.
This is nice explanation. But server cant decrypt MD5 hash. Server has access to all the information to create MD5 hash. It creates MD5 hash using same algorithm and if both the hash matches then we are good to go.